Phylogenetic evidence for the early evolution of microcystin synthesis
- PMID: 14701903
- PMCID: PMC327188
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0304489101
Phylogenetic evidence for the early evolution of microcystin synthesis
Abstract
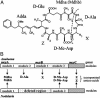
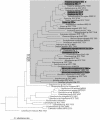
Cyanobacteria are a prolific source of secondary metabolites, including compounds with toxic and enzyme-inhibiting activities. Microcystins and nodularins are the end products of a secondary metabolic pathway comprised of mixed polyketide synthases and nonribosomal peptide synthetases. Both peptides are potent natural toxins produced by distantly related genera of cyanobacteria. Horizontal gene transfer is thought to play a role in the sporadic distribution of microcystin producers among cyanobacteria. Our phylogenetic analyses indicate a coevolution of housekeeping genes and microcystin synthetase genes for the entire evolutionary history of the toxin. Hence they do not corroborate horizontal transfer of genes for microcystin biosynthesis between the genera. The sporadic distribution of microcystin synthetase genes in modern cyanobacteria suggests that the ability to produce the toxin has been lost repeatedly in the more derived lineages of cyanobacteria. The data we present here strongly suggest that the genes encoding nodularin synthetase are recently derived from those encoding microcystin synthetase.
Figures

References
-
- Francis, G. (1878) Nature 18, 11–12.
-
- Sivonen, K. & Jones, G. (1999) in Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water: A Guide to Their Public Health Consequences, Monitoring, and Management, eds. Chorus, I. & Bartram, J. (Spoon, London), pp. 41–111.
-
- Ressom, R., Soong, F. S., Fitzgerald, J., Turczynowicz, L., El Saadi, O., Roder, D., Maynard, T. & Falconer, I. (1994) Health Effects of Toxic Cyanobacteria (Blue-Green Algae) (National Health and Medical Research Council, Australian Government Publishing Service, Canberra), p. 108.
-
- Kuiper-Goodman, T., Falconer, I. & Fitzgerald, J. (1999) in Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water: A Guide to Their Public Health Consequences, Monitoring, and Management, eds. Chorus, I. & Bartram, J. (Spoon, London), pp. 113–153.
-
- Jochimsen, E. M., Carmichael, W. W., An, J., Cardo, D. M., Cookson, S. T., Holmes, C. E. M., Antunes, M. B., de Melo Filho, D. A., Lyra, T. M., Barret, V. S. T., et al. (1998) N. Engl. J. Med. 338, 873–878. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

