Bacillus subtilis RecU protein cleaves Holliday junctions and anneals single-stranded DNA
- PMID: 14701911
- PMCID: PMC327168
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2533829100
Bacillus subtilis RecU protein cleaves Holliday junctions and anneals single-stranded DNA
Erratum in
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Jan 13;106(2):664.. Doncel, Ernesto [corrected to Doncel-Perez, Ernesto]
Abstract
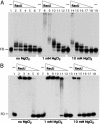
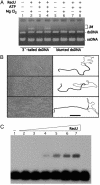
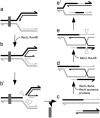
Bacillus subtilis RecU protein is involved in homologous recombination, DNA repair, and chromosome segregation. Purified RecU binds preferentially to three- and four-strand junctions when compared to single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) and double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) ( approximately 10- and approximately 40-fold lower efficiency, respectively). RecU cleaves mobile four-way junctions but fails to cleave a linear dsDNA with a putative cognate site, a finding consistent with a similar genetic defect observed for genes classified within the epsilon epistatic group (namely ruvA, recD, and recU). In the presence of Mg(2+), RecU also anneals a circular ssDNA and a homologous linear dsDNA with a ssDNA tail and a linear ssDNA and a homologous supercoiled dsDNA substrate. These results suggest that RecU, which cleaves recombination intermediates with high specificity, might also help in their assembly.
Figures


References
-
- Kowalczykowski, S. C. (2000) Trends Biochem. Sci. 25, 156–165. - PubMed
-
- Michel, B. (2000) Trends Biochem. Sci. 25, 173–178. - PubMed
-
- Cox, M. M., Goodman, M. F., Kreuzer, K. N., Sherratt, D. J., Sandler, S. J. & Marians, K. J. (2000) Nature 404, 37–41. - PubMed
-
- McGlynn, P. & Lloyd, R. G. (2002) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 3, 859–870. - PubMed
-
- McGlynn, P. & Lloyd, R. G. (2002) Trends Genet. 18, 413–419. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

