Stat-3 is required for pulmonary homeostasis during hyperoxia
- PMID: 14702106
- PMCID: PMC300770
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI19491
Stat-3 is required for pulmonary homeostasis during hyperoxia
Abstract
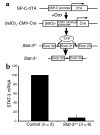
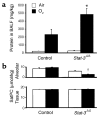
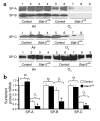
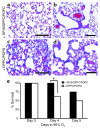
Acute lung injury syndromes remain common causes of morbidity and mortality in adults and children. Cellular and physiologic mechanisms maintaining pulmonary homeostasis during lung injury remain poorly understood. In the present study, the Stat-3 gene was selectively deleted in respiratory epithelial cells by conditional expression of Cre-recombinase under control of the surfactant protein C gene promoter. Cell-selective deletion of Stat-3 in respiratory epithelial cells did not alter prenatal lung morphogenesis or postnatal lung function. However, exposure of adult Stat-3-deleted mice to 95% oxygen caused a more rapidly progressive lung injury associated with alveolar capillary leak and acute respiratory distress. Epithelial cell injury and inflammatory responses were increased in the Stat-3-deleted mice. Surfactant proteins and lipids were decreased or absent in alveolar lavage material. Intratracheal treatment with exogenous surfactant protein B improved survival and lung histology in Stat-3-deleted mice during hyperoxia. Expression of Stat-3 in respiratory epithelial cells is not required for lung formation, but plays a critical role in maintenance of surfactant homeostasis and lung function during oxygen injury.
Figures






References
-
- Akira S. IL-6-regulated transcription factors. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1997;29:1401–1418. - PubMed
-
- Darnell JE., Jr STATs and gene regulation. Science. 1997;277:1630–1635. - PubMed
-
- Boccaccio C, et al. Induction of epithelial tubules by growth factor HGF depends on the STAT pathway. Nature. 1998;391:285–288. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

