Inhibition of growth hormone action improves insulin sensitivity in liver IGF-1-deficient mice
- PMID: 14702113
- PMCID: PMC300761
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI17763
Inhibition of growth hormone action improves insulin sensitivity in liver IGF-1-deficient mice
Abstract
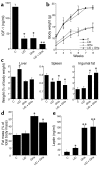
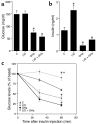
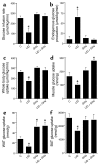
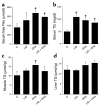
Liver IGF-1-deficient (LID) mice have a 75% reduction in circulating IGF-1 levels and, as a result, a fourfold increase in growth hormone (GH) secretion. To block GH action, LID mice were crossed with GH antagonist (GHa) transgenic mice. Inactivation of GH action in the resulting LID + GHa mice led to decreased blood glucose and insulin levels and improved peripheral insulin sensitivity. Hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp studies showed that LID mice exhibit severe insulin resistance. In contrast, expression of the GH antagonist transgene in LID + GHa mice led to enhanced insulin sensitivity and increased insulin-stimulated glucose uptake in muscle and white adipose tissue. Interestingly, LID + GHa mice exhibit a twofold increase in white adipose tissue mass, as well as increased levels of serum-free fatty acids and triglycerides, but no increase in the triglyceride content of liver and muscle. In conclusion, these results show that despite low levels of circulating IGF-1, insulin sensitivity in LID mice could be improved by inactivating GH action, suggesting that chronic elevation of GH levels plays a major role in insulin resistance. These results suggest that IGF-1 plays a role in maintaining a fine balance between GH and insulin to promote normal carbohydrate and lipid metabolism.
Figures



Comment in
-
The relative roles of growth hormone and IGF-1 in controlling insulin sensitivity.J Clin Invest. 2004 Jan;113(1):25-7. doi: 10.1172/JCI20660. J Clin Invest. 2004. PMID: 14702105 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Houssay BA. The hypophysis and metabolism. N. Engl. J. Med. 1936;214:961.
-
- Moller N, et al. Effects of growth hormone on glucose metabolism. Horm. Res. 1991;36(Suppl 1):32–35. - PubMed
-
- Davidson MB. Effect of growth hormone on carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Endocr. Rev. 1987;8:115–131. - PubMed
-
- Beauville M, et al. Effect of long-term rhGH administration in GH-deficient adults on fat cell epinephrine response. Am. J. Physiol. 1992;263:E467–E472. - PubMed
-
- Kamel A, Norgren S, Elimam A, Danielsson P, Marcus C. Effects of growth hormone treatment in obese prepubertal boys. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000;85:1412–1419. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

