The sorbitol phosphotransferase system is responsible for transport of 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol into Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium
- PMID: 14702317
- PMCID: PMC305747
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.186.2.473-480.2004
The sorbitol phosphotransferase system is responsible for transport of 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol into Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium
Abstract
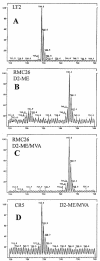
2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate is the first committed intermediate in the biosynthesis of the isoprenoid precursors isopentenyl diphosphate and dimethylallyl diphosphate. Supplementation of the growth medium with 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol has been shown to complement disruptions in the Escherichia coli gene for 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase, the enzyme that synthesizes the immediate precursor of 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate. In order to be utilized in isoprenoid biosynthesis, 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol must be phosphorylated. We describe the construction of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium strain RMC26, in which the essential gene encoding 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase has been disrupted by insertion of a synthetic mevalonate operon consisting of the yeast ERG8, ERG12, and ERG19 genes, responsible for converting mevalonate to isopentenyl diphosphate under the control of an arabinose-inducible promoter. Random mutagenesis of RMC26 produced defects in the sorbitol phosphotransferase system that prevented the transport of 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol into the cell. RMC26 and mutant strains of RMC26 unable to grow on 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol were incubated in buffer containing mevalonate and deuterium-labeled 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol. Ubiquinone-8 was isolated from these cells and analyzed for deuterium content. Efficient incorporation of deuterium was observed for RMC26. However, there was no evidence of deuterium incorporation into the isoprenoid side chain of ubiquinone Q8 in the RMC26 mutants.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Deuterium-labelled isotopomers of 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol as tools for the elucidation of the 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate pathway for isoprenoid biosynthesis.Biochem J. 2000 Mar 15;346 Pt 3(Pt 3):737-42. Biochem J. 2000. PMID: 10698701 Free PMC article.
-
Escherichia coli engineered to synthesize isopentenyl diphosphate and dimethylallyl diphosphate from mevalonate: a novel system for the genetic analysis of the 2-C-methyl-d-erythritol 4-phosphate pathway for isoprenoid biosynthesis.Biochem J. 2001 Jan 1;353(Pt 1):59-67. Biochem J. 2001. PMID: 11115399 Free PMC article.
-
A 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase catalyzing the formation of 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate in an alternative nonmevalonate pathway for terpenoid biosynthesis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Aug 18;95(17):9879-84. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.17.9879. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998. PMID: 9707569 Free PMC article.
-
Isoprenoid biosynthesis via 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate/2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate (DOXP/MEP) pathway.Acta Biochim Pol. 2001;48(3):663-72. Acta Biochim Pol. 2001. PMID: 11833775 Review.
-
Non-mevalonate isoprenoid biosynthesis: enzymes, genes and inhibitors.Biochem Soc Trans. 2000 Dec;28(6):785-9. Biochem Soc Trans. 2000. PMID: 11171208 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of novel small molecule inhibitors of 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol (CDP-ME) kinase of Gram-negative bacteria.Bioorg Med Chem. 2011 Oct 1;19(19):5886-95. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2011.08.012. Epub 2011 Aug 16. Bioorg Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21903402 Free PMC article.
-
Sub-inhibitory fosmidomycin exposures elicits oxidative stress in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium LT2.PLoS One. 2014 Apr 21;9(4):e95271. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0095271. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24751777 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the antimicrobial activity of pantothenamides against uropathogenic Escherichia coli.Microbiol Spectr. 2025 Aug 5;13(8):e0306924. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03069-24. Epub 2025 Jun 23. Microbiol Spectr. 2025. PMID: 40548707 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic Routes to Methylerythritol Phosphate Pathway Intermediates and Downstream Isoprenoids.Curr Org Chem. 2014 Apr;18(8):1050-1072. doi: 10.2174/1385272819666140501001101. Curr Org Chem. 2014. PMID: 25009443 Free PMC article.
-
Formal Synthesis of 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl D-erythritol From D-(+)-Arabitol.Tetrahedron. 2012 Oct 28;68(43):8937-8941. doi: 10.1016/j.tet.2012.08.020. Tetrahedron. 2012. PMID: 23049145 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agranoff, B. W., H. Eggerer, U. Henning, and F. Lynen. 1959. Isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 81:1254-1255. - PubMed
-
- Altincicek, B., E. C. Duin, A. Reichenberg, R. Hedderich, A. K. Kollas, M. Hintz, S. Wagner, J. Wiesner, E. Beck, and H. Jomaa. 2002. LytB protein catalyzes the terminal step of the 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol-4-phosphate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthesis. FEBS Lett. 532:437-440. - PubMed
-
- Altincicek, B., A. Kollas, M. Eberl, J. Wiesner, S. Sanderbrand, M. Hintz, E. Beck, and H. Jomaa. 2001. LytB, a novel gene of the 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 499:37-40. - PubMed
-
- Amdur, B. H., H. Rilling, and K. Bloch. 1957. The enzymatic conversion of mevalonic acid to squalene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 79:2646-2647.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

