Regulation of synaptojanin 1 by cyclin-dependent kinase 5 at synapses
- PMID: 14704270
- PMCID: PMC327184
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0307813100
Regulation of synaptojanin 1 by cyclin-dependent kinase 5 at synapses
Abstract
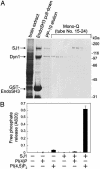
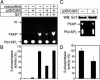
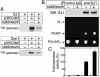
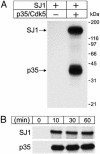
Synaptojanin 1 is a polyphosphoinositide phosphatase concentrated in presynaptic nerve terminals, where it dephosphorylates a pool of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate implicated in synaptic vesicle recycling. Like other proteins with a role in endocytosis, synaptojanin 1 undergoes constitutive phosphorylation in resting synapses and stimulation-dependent dephosphorylation by calcineurin. Here, we show that cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (Cdk5) phosphorylates synaptojanin 1 and regulates its function both in vitro and in intact synaptosomes. Cdk5 phosphorylation inhibited the inositol 5-phosphatase activity of synaptojanin 1, whereas dephosphorylation by calcineurin stimulated such activity. The activity of synaptojanin 1 was also stimulated by its interaction with endophilin 1, its major binding partner at the synapse. Notably, Cdk5 phosphorylated serine 1144, which is adjacent to the endophilin binding site. Mutation of serine 1144 to aspartic acid to mimic phosphorylation by Cdk5 inhibited the interaction of synaptojanin 1 with endophilin 1. These results suggest that Cdk5 and calcineurin may have an antagonistic role in the regulation of synaptojanin 1 recruitment and activity, and therefore in the regulation of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate turnover at synapses.
Figures
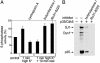

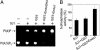
Comment in
-
Protein kinases talk to lipid phosphatases at the synapse.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Feb 3;101(5):1112-3. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0308374101. Epub 2004 Jan 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 14745021 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- De Camilli, P., Emr, S. D., McPherson, P. S. & Novick, P. (1996) Science 271, 1533–1539. - PubMed
-
- Martin, T. F. J. (1998) Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 14, 231–264. - PubMed
-
- Takenawa, T. & Itoh, T. (2001) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1533, 190–206. - PubMed
-
- Yin, H. L. & Janmey, P. A. (2003) Annu. Rev. Physiol. 65, 761–789. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

