Conditional targeting of E-cadherin in skin: insights into hyperproliferative and degenerative responses
- PMID: 14704278
- PMCID: PMC327185
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0307437100
Conditional targeting of E-cadherin in skin: insights into hyperproliferative and degenerative responses
Abstract
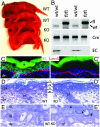
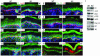
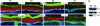
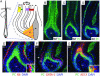
Loss of E-cadherin has been associated with human cancers, and yet in the early mouse embryo and the lactating mammary gland, the E-cadherin null state results in tissue dysfunction and cell death. Here we targeted loss of E-cadherin in skin epithelium. The epidermal basal layer responded by elevating P-cadherin, enabling these cells to maintain adherens junctions. Suprabasal layers upregulated desmosomal cadherins, but without classical cadherins, terminal differentiation was impaired. Progressive hyperplasia developed with age, a possible consequence of proliferative maintenance in basal cells coupled with defects in terminal differentiation. In contrast, hair follicles lost integrity of the inner root sheath and hair cuticle without apparent elevation of cadherins. These findings suggest that, if no compensatory mechanisms exist, E-cadherin loss may be incompatible with epithelial tissue survival, whereas partial compensation can result in alterations in differentiation and proliferation.
Figures


References
-
- Perez-Moreno, M., Jamora, C. & Fuchs, E. (2003) Cell 112, 535–548. - PubMed
-
- Kowalczyk, A. P., Bornslaeger, E. A., Norvell, S. M., Palka, H. L. & Green, K. J. (1999) Int. Rev. Cytol. 185, 237–302. - PubMed
-
- Vasioukhin, V., Bowers, E., Bauer, C., Degenstein, L. & Fuchs, E. (2001) Nat. Cell Biol. 3, 1076–1085. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

