Recombinant immunotoxins and retargeted killer cells: employing engineered antibody fragments for tumor-specific targeting of cytotoxic effectors
- PMID: 14704833
- PMCID: PMC11034274
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-003-0482-8
Recombinant immunotoxins and retargeted killer cells: employing engineered antibody fragments for tumor-specific targeting of cytotoxic effectors
Abstract
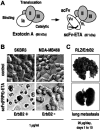
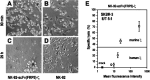
Over the past years, monoclonal antibodies have attracted enormous interest as targeted therapeutics, and a number of such reagents are in clinical use. However, responses could not be achieved in all patients with tumors expressing high levels of the respective target antigens, suggesting that other factors such as limited recruitment of endogenous immune effector mechanisms can also influence treatment outcome. This justifies the search for alternative, potentially more effective reagents. Antibody-toxins and cytolytic effector cells genetically modified to carry antibody-based receptors on the surface, represent such tailor-made targeting vehicles with the potential of improved tumor localization and enhanced efficacy. In this way, advances in recombinant antibody technology have made it possible to circumvent problems inherent in chemical coupling of antibodies and toxins, and have allowed construction via gene fusion of recombinant molecules which combine antibody-mediated recognition of tumor cells with specific delivery of potent protein toxins of bacterial or plant origin. Likewise, recombinant antibody fragments provide the basis for the construction of chimeric antigen receptors that, upon expression in cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) or natural killer (NK) cells, link antibody-mediated recognition of tumor antigens with these effector cells' potent cytolytic activities, thereby making them promising cellular therapeutics for adoptive cancer therapy. Here, general principles for the derivation of cytotoxic proteins and effector cells with antibody-dependent tumor specificity are summarized, and current strategies to employ these molecules and cells for directed cancer therapy are discussed, focusing mainly on the tumor-associated antigens epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and the closely related ErbB2 (HER2) as targets.
Figures
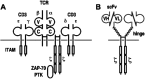
References
-
- Altenschmidt Clin Cancer Res. 1996;2:1001. - PubMed
-
- Altenschmidt J Immunol. 1997;159:5509. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez-Vallina Eur J Immunol. 1996;26:2304. - PubMed
-
- Azemar M, Djahansouzi S, Jäger E, Solbach C, Schmidt M, Maurer AB, Mross K, Unger C, Minckwitz G, Dall P, Groner B, Wels W. Regression of cutaneous tumor lesions in patients intratumorally injected with a recombinant single-chain antibody-toxin targeted to ErbB2/HER2. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment. 2003;82:155–164. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

