Self-gated cardiac cine MRI
- PMID: 14705049
- PMCID: PMC2396326
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.10664
Self-gated cardiac cine MRI
Abstract
The need for ECG gating presents many difficulties in cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (CMRI). Real-time imaging techniques eliminate the need for ECG gating in cine CMRI, but they cannot offer the spatial and temporal resolution provided by segmented acquisition techniques. Previous MR signal-based techniques have demonstrated an ability to provide cardiac gating information; however, these techniques result in decreased imaging efficiency. The purpose of this work was to develop a new "self-gated" (SG) acquisition technique that eliminates these efficiency deficits by extracting the motion synchronization signal directly from the same MR signals used for image reconstruction. Three separate strategies are proposed for deriving the SG signal from data acquired using radial k-space sampling: echo peak magnitude, kymogram, and 2D correlation. The SG techniques were performed on seven normal volunteers. A comparison of the results showed that they provided cine image series with no significant differences in image quality compared to that obtained with conventional ECG gating techniques. SG techniques represent an important practical advance in clinical MRI because they enable the acquisition of high temporal and spatial resolution cardiac cine images without the need for ECG gating and with no loss in imaging efficiency.
Copyright 2003 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
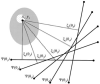
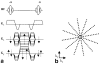
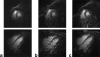


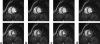

References
-
- Rokey R, Wendt R, Johnston D. Monitoring of acutely ill patients during nuclear magnetic resonance imaging: use of a time-varying filter electorcardiographic gating device to reduce gradient artifacts. Magn Reson Med. 1988;6:240–245. - PubMed
-
- Polson M, Barker A, Gardiner S. The effect of rapid rise-time magnetic fields on the ECG of the rat. Clin Phys Physiol Meas. 1982;3:231–234. - PubMed
-
- Shetty A. Suppression of radiofrequency interference in cardiac gated MRI: a simple design. Magn Reson Med. 1988;8:84–88. - PubMed
-
- Damji A, Snyder R, Ellinger D, Witkowski F, Allen P. RF Interference suppression in a cardiac synchronization system operating in a high magnetic field NMR imaging system. Magn Reson Imaging. 1988;6:637–640. - PubMed
-
- Dimick R, Hedlund L, Herfkens R, Fram E, Utz J. Optimizing ECG electrode placement for cardiac-gated magnetic resonance imaging. Invest Radiol. 1986;22:17–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

