Schnurri-3 (KRC) interacts with c-Jun to regulate the IL-2 gene in T cells
- PMID: 14707112
- PMCID: PMC1887724
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20030421
Schnurri-3 (KRC) interacts with c-Jun to regulate the IL-2 gene in T cells
Abstract
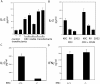
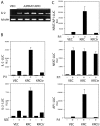
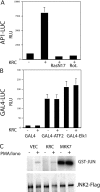
The activator protein 1 (AP-1) transcription factor is a key participant in the control of T cell proliferation, cytokine production, and effector function. In the immune system, AP-1 activity is highest in T cells, suggesting that a subset of T cell-specific coactivator proteins exist to selectively potentiate AP-1 function. Here, we describe that the expression of Schnurri-3, also known as kappa recognition component (KRC), is induced upon T cell receptor signaling in T cells and functions to regulate the expression of the interleukin 2 (IL-2) gene. Overexpression of KRC in transformed and primary T cells leads to increased IL-2 production, whereas dominant-negative KRC, or loss of KRC protein in KRC-null mice, results in diminished IL-2 production. KRC physically associates with the c-Jun transcription factor and serves as a coactivator to augment AP-1-dependent IL-2 gene transcription.
Figures

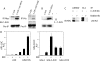
References
-
- Wu, L.C., Y. Liu, J. Strandtmann, C.H. Mak, B. Lee, Z. Li, and C.Y. Yu. 1996. The mouse DNA binding protein Rc for the kappa B motif of transcription and for the V(D)J recombination signal sequences contains composite DNA-protein interaction domains and belongs to a new family of large transcriptional proteins. Genomics. 35:415–424. - PubMed
-
- Hicar, M.D., M.L. Robinson, and L.C. Wu. 2002. Embryonic expression and regulation of the large zinc finger protein KRC. Genesis. 33:8–20. - PubMed
-
- Mak, C.H., Z. Li, C.E. Allen, Y. Liu, and L. Wu. 1998. KRC transcripts: identification of an unusual alternative splicing event. Immunogenetics. 48:32–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

