Increased expression of interleukin 23 p19 and p40 in lesional skin of patients with psoriasis vulgaris
- PMID: 14707118
- PMCID: PMC1887731
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20030451
Increased expression of interleukin 23 p19 and p40 in lesional skin of patients with psoriasis vulgaris
Abstract
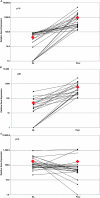
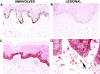
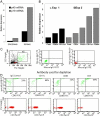
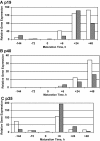
Psoriasis is a type I-deviated disease characterized by the presence of interferon (IFN)-gamma and multiple IFN-related inflammatory genes in lesions. Because interleukin (IL)-23 is now recognized to play a role in the recruitment of inflammatory cells in a T helper cell (Th)1-mediated disease, we examined psoriasis skin lesions for production of this newly described cytokine. IL-23 is composed of two subunits: a unique p19 subunit and a p40 subunit shared with IL-12. We found a reliable increase in p19 mRNA by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction in lesional skin compared with nonlesional skin (22.3-fold increase; P = 0.001). The p40 subunit, shared by IL-12 and IL-23, increased by 11.6-fold compared with nonlesional skin (P = 0.003), but the IL-12 p35 subunit was not increased in lesional skin. IL-23 was expressed mainly by dermal cells and increased p40 immunoreactivity was visualized in large dermal cells in the lesions. Cell isolation experiments from psoriatic tissue showed strong expression of p19 mRNA in cells expressing monocyte (CD14+ CD11c+ CD83-) and mature dendritic cell (DC) markers (CD14- CD11c+ CD83+), whereas in culture, the mRNAs for p40 and p19 were strongly up-regulated in stimulated monocytes and monocyte-derived DCs, persisting in the latter for much longer periods than IL-12. Our data suggest that IL-23 is playing a more dominant role than IL-12 in psoriasis, a Th1 type of human inflammatory disease.
Figures
References
-
- Oppmann, B., R. Lesley, B. Blom, J.C. Timans, Y. Xu, B. Hunte, F. Vega, N. Yu, J. Wang, K. Singh, et al. 2000. Novel p19 protein engages IL-12p40 to form a cytokine, IL-23, with biological activities similar as well as distinct from IL-12. Immunity. 13:715–725. - PubMed
-
- Parham, C., M. Chirica, J. Timans, E. Vaisberg, M. Travis, J. Cheung, S. Pflanz, R. Zhang, K.P. Singh, F. Vega, et al. 2002. A receptor for the heterodimeric cytokine IL-23 is composed of IL-12Rbeta1 and a novel cytokine receptor subunit, IL-23R. J. Immunol. 168:5699–5708. - PubMed
-
- Wiekowski, M.T., M.W. Leach, E.W. Evans, L. Sullivan, S.C. Chen, G. Vassileva, J.F. Bazan, D.M. Gorman, R.A. Kastelein, S. Narula, et al. 2001. Ubiquitous transgenic expression of the IL-23 subunit p19 induces multiorgan inflammation, runting, infertility, and premature death. J. Immunol. 166:7563–7570. - PubMed
-
- Cua, D.J., J. Sherlock, Y. Chen, C.A. Murphy, B. Joyce, B. Seymour, L. Lucian, W. To, S. Kwan, T. Churakova, et al. 2003. Interleukin-23 rather than interleukin-12 is the critical cytokine for autoimmune inflammation of the brain. Nature. 421:744–748. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

