Comparison of evoked arousability in breast and formula fed infants
- PMID: 14709496
- PMCID: PMC1755888
Comparison of evoked arousability in breast and formula fed infants
Abstract
Background: Currently, there is no consistent evidence that breast feeding reduces the risk for sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS). Arousal from sleep is believed to be an important survival mechanism that may be impaired in victims of SIDS. Previously it has been shown that arousability is impaired by the major risk factors for SIDS such as prone sleeping and maternal smoking.
Aims: To establish whether arousability was altered by method of feeding, and whether breast fed infants would have lower arousal thresholds.
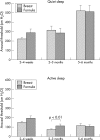
Methods: Forty three healthy term infants were studied using daytime polysomnography on three occasions: 2-4 weeks post-term, 2-3 months post-term, and 5-6 months post-term. Multiple measurements of arousal threshold (cm H(2)O) in response to nasal air jet stimulation applied alternately to the nares were made in both active sleep (AS) and quiet sleep (QS) while infants slept supine. Arousal thresholds and sleep period lengths were compared between formula fed and breast fed infants at each age.
Results: Arousal thresholds were not different between breast fed and formula fed infants in QS. However, in AS breast fed infants were significantly more arousable than formula fed infants at 2-3 months of age. There was no difference between groups of infants when sleep period length was compared at any study.
Conclusions: Breast fed infants are more easily aroused from AS at 2-3 months of age than formula fed infants. This age coincides with the peak incidence of SIDS.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials