Role of the hydrophobic domain in targeting caveolin-1 to lipid droplets
- PMID: 14709541
- PMCID: PMC2171963
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200303037
Role of the hydrophobic domain in targeting caveolin-1 to lipid droplets
Abstract
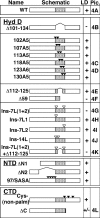
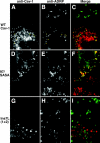
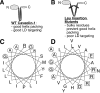
Although caveolins normally reside in caveolae, they can accumulate on the surface of cytoplasmic lipid droplets (LDs). Here, we first provided support for our model that overaccumulation of caveolins in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) diverts the proteins to nascent LDs budding from the ER. Next, we found that a mutant H-Ras, present on the cytoplasmic surface of the ER but lacking a hydrophobic peptide domain, did not accumulate on LDs. We used the fact that wild-type caveolin-1 accumulates in LDs after brefeldin A treatment or when linked to an ER retrieval motif to search for mutants defective in LD targeting. The hydrophobic domain, but no specific sequence therein, was required for LD targeting of caveolin-1. Certain Leu insertions blocked LD targeting, independently of hydrophobic domain length, but dependent on their position in the domain. We propose that proper packing of putative hydrophobic helices may be required for LD targeting of caveolin-1.
Figures






References
-
- Abell, B.M., S. High, and M.M. Moloney. 2002. Membrane topology of oleosin is constrained by its long hydrophobic domain. J. Biol. Chem. 277:8602–8610. - PubMed
-
- Arbuzova, A., L. Wang, J. Wang, G. Hangyas-Mihalyne, D. Murray, B. Honig, and S. McLaughlin. 2000. Membrane binding of peptides containing both basic and aromatic residues. Experimental studies with peptides corresponding to the scaffolding region of caveolin and the effector region of MARCKS. Biochemistry. 39:10330–10339. - PubMed
-
- Arreaza, G., and D.A. Brown. 1995. Sorting and intracellular trafficking of a glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored protein and two hybrid proteins with the same ectodomain in MDCK kidney epithelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 270:23641–23647. - PubMed
-
- Barba, G., F. Harper, T. Harada, M. Kohara, S. Goulinet, Y. Matsuura, G. Eder, Z. Schaf, M.J. Chapman, T. Miyamura, and C. Brechot. 1997. Hepatitis C virus core protein shows a cytoplasmic localization and associates to cellular lipid storage droplets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 94:1200–1205. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

