A test of the CoHR motif associated with meiotic double-strand breaks in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 14710185
- PMCID: PMC1298961
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400050
A test of the CoHR motif associated with meiotic double-strand breaks in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
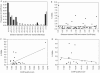
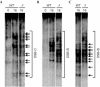
Meiotic recombination is not random along chromosomes; rather, there are preferred regions for initiation called hotspots. Although the general properties of meiotic hotspots are known, the requirements at the DNA sequence level for the determination of hotspot activity are still unclear. The sequence of six known hotspots in Saccharomyces cerevisiae was compared to identify a common homology region (CoHR). They reported that the locations of CoHR sequences correspond to mapped double-strand break (DSB) sites along three chromosomes (I, III, VI). We report here that a deletion of CoHR at HIS2, a hotspot used to identify the motif, has no significant effect on recombination. In the absence of CoHR, DSB formation occurs at a high frequency and at the same sequences as in wild-type strains. In cases where the deletion of sequences containing the CoHR motif has been shown to reduce recombination, we propose that it may be a reflection of the location of the deletion, rather than the loss of CoHR, per se.
Figures


References
-
- Alani E, Padmore R, Kleckner N (1990) Analysis of wild-type and rad50 mutants of yeast suggests an intimate relationship between meiotic chromosome synapsis and recombination. Cell 61: 419–436 - PubMed
-
- Baker BS, Carpenter AT, Esposito MS, Esposito RE, Sandler L (1976) The genetic control of meiosis. Annu Rev Genet 10: 53–134 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

