MUC1: a multifunctional cell surface component of reproductive tissue epithelia
- PMID: 14711375
- PMCID: PMC320498
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-7827-2-4
MUC1: a multifunctional cell surface component of reproductive tissue epithelia
Abstract
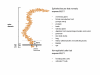
MUC1 is a large, transmembrane mucin glycoprotein expressed at the apical surface of a variety of reproductive tract epithelia. Functions attributed to MUC1 include those generally associated with mucins such as lubrication and hydration of cell surfaces as well as protection from microorganisms and degradative enzymes. In addition, MUC1 is an effective inhibitor of both cell-cell and cell-extracellular matrix interactions in both normal and malignant contexts. Moreover, a series of recent studies has shown that the highly conserved cytoplasmic tail of MUC1 interacts specifically with a series of important signal transducing molecules including beta-catenin, Grb2 and erbB family members. MUC1 expression in normal epithelia can be quite dynamic, varying in response to steroid hormone or cytokine influences. Following malignant transformation, MUC1 often becomes highly overexpressed, loses its apical restriction, and displays aberrant glycosylation and altered mRNA splice variants. Regulation of MUC1 expression can occur at the transcriptional level. In addition, post-translational regulation of cell surface expression occurs via the activity of cell surface proteases or "sheddases" that release soluble forms of the large ectodomains. This review will briefly summarize studies of MUC1 expression and function in reproductive tissues with particular emphasis on the uterus. In addition, current knowledge of the mechanisms of MUC1 gene regulation, metabolic processing and potential signal transducing functions will be presented.
Figures


References
-
- Gendler SJ, Spicer AP. Epithelial mucin genes. Annu Rev Physiol. 1995;57:607–634. - PubMed
-
- Lagow E, DeSouza MM, Carson DD. Mammalian reproductive tract mucins. Hum Reprod Update. 1999;5:280–292. - PubMed
-
- Williams SJ, Wreschner DH, Tran M, Eyre HJ, Sutherland GR, McGuckin MA. Muc13, a novel human cell surface mucin expressed by epithelial and hemopoietic cells. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:18327–18336. - PubMed
-
- Vimal DB, Khullar M, Gupta S, Ganguly NK. Intestinal mucins: the binding sites for Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Cell Biochem. 2000;204:107–117. - PubMed
-
- Lillehoj EP, Kim BT, Kim KC. Identification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa flagellin as an adhesin for Muc1 mucin. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2002;282:L751–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

