Characterization of a new erm-related macrolide resistance gene present in probiotic strains of Bacillus clausii
- PMID: 14711653
- PMCID: PMC321311
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.70.1.280-284.2004
Characterization of a new erm-related macrolide resistance gene present in probiotic strains of Bacillus clausii
Abstract
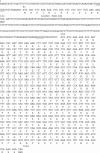
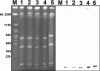
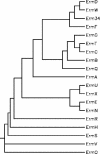
The mechanism of resistance to macrolides, lincosamides, and streptogramins B was studied in four Bacillus clausii strains that are mixed in a probiotic administered to humans for prevention of gastrointestinal side effects due to oral antibiotic chemotherapy and in three reference strains of B. clausii, DSM8716, ATCC 21536, and ATCC 21537. An 846-bp gene called erm(34), which is related to the erm genes conferring resistance to these antibiotics by ribosomal methylation, was cloned from total DNA of B. clausii DSM8716 into Escherichia coli. The deduced amino acid sequence presented 61% identity with that of Erm(D) from B. licheniformis, B. halodurans, and B. anthracis. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of total DNA digested by I-CeuI, followed by hybridization with an erm(34)-specific probe, indicated a chromosomal location of the gene in all B. clausii strains. Repeated attempts to transfer resistance to macrolides by conjugation from B. clausii strains to Enterococcus faecalis JH2-2, E. faecium HM1070, and B. subtilis UCN19 were unsuccessful.
Figures
References
-
- Angot, P., M. Vergnaud, M. Auzou, R. Leclercq, and Observatoire de Normandie du Pneumocoque. 2000. Macrolide resistance phenotypes and genotypes in French clinical isolates of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 19:755-758. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

