Gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) and IFN-gamma-inducing cytokines interleukin-12 (IL-12) and IL-18 do not augment infection-stimulated bone resorption in vivo
- PMID: 14715554
- PMCID: PMC321357
- DOI: 10.1128/cdli.11.1.106-110.2004
Gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) and IFN-gamma-inducing cytokines interleukin-12 (IL-12) and IL-18 do not augment infection-stimulated bone resorption in vivo
Abstract
Periapical granulomas are induced by bacterial infection of the dental pulp and result in destruction of the surrounding alveolar bone. In previous studies we have reported that the bone resorption in this model is primarily mediated by macrophage-expressed interleukin-1 (IL-1). The expression and activity of IL-1 is in turn modulated by a network of Th1 and Th2 regulatory cytokines. In the present study, the functional roles of the Th1 cytokine gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) and IFN-gamma-inducing cytokines IL-12 and IL-18 were determined in a murine model of periapical bone destruction. IL-12-/-, IL-18-/-, and IFN-gamma-/- mice were subjected to surgical pulp exposure and infection with a mixture of four endodontic pathogens, and bone destruction was determined by microcomputed tomography on day 21. The results indicated that all IL-12-/-, IL-18-/-, and IFN-gamma-/- mice had similar infection-stimulated bone resorption in vivo as wild-type control mice. Mice infused with recombinant IL-12 also had resorption similar to controls. IFN-gamma-/- mice exhibited significant elevations in IL-6, IL-10, IL-12, and tumor necrosis factor alpha in lesions compared to wild-type mice, but these modulations had no net effect on IL-1alpha levels. Recombinant IL-12, IL-18, and IFN-gamma individually failed to consistently modulate macrophage IL-1alpha production in vitro. We conclude that, at least individually, endogenous IL-12, IL-18, and IFN-gamma do not have a significant effect on the pathogenesis of infection-stimulated bone resorption in vivo, suggesting possible functional redundancy in proinflammatory pathways.
Figures


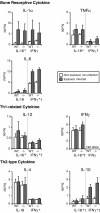
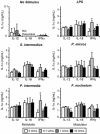
References
-
- Balto, K., R. Müller, D. C. Carrington, J. Dobeck, and P. Stashenko. 2000. Quantification of periapical bone destruction in mice by micro-computed tomography. J. Dent. Res. 79:35-40. - PubMed
-
- Boraschi, D., S. Censini, and A. Tagliabue. 1984. Interferon-gamma reduces macrophage-suppressive activity by inhibiting prostaglandin E2 release and inducing interleukin 1 production. J. Immunol. 133:764-768. - PubMed
-
- Chan, S. H., B. Perussia, J. W. Gupta, M. Kobayashi, M. Pospisil, H. A. Young, S. F. Wolf, D. Young, S. C. Clark, and G. Trinchieri. 1991. Induction of interferon gamma production by natural killer cell stimulatory factor: characterization of the responder cells and synergy with other inducers. J. Exp. Med. 173:869-879. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dalton, D. K., S. Pitts-Meek, S. Keshav, I. S. Figari, A. Bradley, and T. A. Stewart. 1993. Multiple defects of immune cell function in mice with disrupted interferon-gamma genes. Science 259:1739-1742. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

