Development of an immunochromatographic test with recombinant EMA-2 for the rapid detection of antibodies against Babesia equi in horses
- PMID: 14715778
- PMCID: PMC321651
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.42.1.359-361.2004
Development of an immunochromatographic test with recombinant EMA-2 for the rapid detection of antibodies against Babesia equi in horses
Abstract
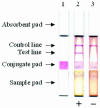
An immunochromatographic test (BeICT) for the rapid detection of antibodies against Babesia equi was developed. It clearly differentiated B. equi-infected horses from B. caballi-infected and uninfected horses. The agreement with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay results was 96.7% in the detection of field sera. The results suggest that BeICT is rapid, simple, reliable, and suitable for use to detect B. equi infection in the field.
Figures

References
-
- Bose, R. W. K. Jorgensen, R. J. Dalgliesh, K. T. Friedhoff, and A. J. de Vos. 1995. Current state and future trends in the diagnosis of babesiosis. Vet. Parasitol. 57:61-74. - PubMed
-
- Bruning, A. 1996. Equine piroplasmosis: an update on diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. Br. Vet. J. 152:139-151. - PubMed
-
- De Waal, D. T. 2000. Global importance of piroplasmosis. J. Protozool. Res. 10:106-127.
-
- Holbrook, A. A. 1969. Biology of equine piroplasmosis. Am. J. Vet. Med. Assoc. 155:453-454. - PubMed
-
- Huang, X., X. Xuan, N. Yokoyama, L. Xu, H. Suzuki, C. Sugimoto, H. Nagasawa, K. Fujisaki, and I. Igarashi. 2003. High-level expression and purification of a truncated merozoite antigen-2 of Babesia equi in Escherichia coli and its potential in immunodiagnosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 41:1147-1151. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

