Fluoroquinolones and the risk for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in hospitalized patients
- PMID: 14718085
- PMCID: PMC3035560
- DOI: 10.3201/eid0911.030284
Fluoroquinolones and the risk for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in hospitalized patients
Abstract
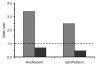
To determine whether fluoroquinolone exposure is a risk factor for the isolation of Staphylococcus aureus and whether the effect is different for methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) versus methicillin--susceptible S. aureus (MSSA), we studied two case groups. The first case group included 222 patients with nosocomially acquired MRSA. The second case group included 163 patients with nosocomially acquired MSSA. A total of 343 patients admitted concurrently served as controls. Outcome measures were the adjusted odds ratio (OR) for isolation of MRSA and MSSA after fluoroquinolone exposure. Exposure to both levofloxacin (OR 5.4; p <0.0001) and ciprofloxacin (OR 2.2; p < 0.003) was associated with isolation of MRSA but not MSSA. After adjustment for multiple variables, both drugs remained risk factors for MRSA (levofloxacin OR 3.4; p <0.0001; ciprofloxacin OR 2.5; p = 0.005) but not MSSA. Exposure to levofloxacin or ciprofloxacin is a significant risk factor for the isolation of MRSA, but not MSSA.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
