Cowpox with severe generalized eruption, Finland
- PMID: 14718092
- PMCID: PMC3035531
- DOI: 10.3201/eid0911.020814
Cowpox with severe generalized eruption, Finland
Abstract
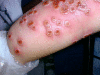
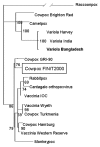
Cowpox with a severe, generalized eruption was diagnosed in an atopic 4-year-old girl by electron microscopy, virus isolation, polymerase chain reaction, and immunoglobulin (Ig) M and low-avidity IgG antibodies. The hemagglutinin gene of the isolate clustered with a Russian cowpox virus strain, and more distantly, with other cowpox and vaccinia virus strains. The patient's dog had orthopoxvirus-specific antibodies, indicating a possible transmission route. In Finnish wild rodents, orthopoxvirus seroprevalences were 0%-92%, in humans the seroprevalence was 100% in the age group >50, decreasing towards younger age groups.
Figures
References
-
- Esposito JJ, Fenner F. Poxviruses. In: Knipe DM, Howley PM, editors. Fields virology. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2001. p. 2885–921.
-
- Jenner E. An inquiry into the causes and effects of the variola vaccine, a disease discovered in some of the western counties of England, particularly Gloucestershire, and known by the name of the cowpox. London: Sampson Low; 1798.
-
- Moss B. Poxviridae: the viruses and their replication. In: Knipe DM, Howley PM, editors. Fields virology. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2001. p. 2849–83.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
