The yeast elongator histone acetylase requires Sit4-dependent dephosphorylation for toxin-target capacity
- PMID: 14718557
- PMCID: PMC363168
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e03-10-0750
The yeast elongator histone acetylase requires Sit4-dependent dephosphorylation for toxin-target capacity
Abstract
Kluyveromyces lactis zymocin, a heterotrimeric toxin complex, imposes a G1 cell cycle block on Saccharomyces cerevisiae that requires the toxin-target (TOT) function of holo-Elongator, a six-subunit histone acetylase. Here, we demonstrate that Elongator is a phospho-complex. Phosphorylation of its largest subunit Tot1 (Elp1) is supported by Kti11, an Elongator-interactor essential for zymocin action. Tot1 dephosphorylation depends on the Sit4 phosphatase and its associators Sap185 and Sap190. Zymocin-resistant cells lacking or overproducing Elongator-associator Tot4 (Kti12), respectively, abolish or intensify Tot1 phosphorylation. Excess Sit4.Sap190 antagonizes the latter scenario to reinstate zymocin sensitivity in multicopy TOT4 cells, suggesting physical competition between Sit4 and Tot4. Consistently, Sit4 and Tot4 mutually oppose Tot1 de-/phosphorylation, which is dispensable for integrity of holo-Elongator but crucial for the TOT-dependent G1 block by zymocin. Moreover, Sit4, Tot4, and Tot1 cofractionate, Sit4 is nucleocytoplasmically localized, and sit4Delta-nuclei retain Tot4. Together with the findings that sit4Delta and totDelta cells phenocopy protection against zymocin and the ceramide-induced G1 block, Sit4 is functionally linked to Elongator in cell cycle events targetable by antizymotics.
Figures
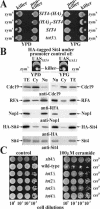
 ) of Tot1 and Tot1-HA are shown by arrows. (B) Phosphorylation of Tot1 requires full-length protein. 9E10 (anti-c-Myc) immunoprecipitates from strains FFY3/1dt (TOT3-(c-myc)3 TOT1-(HA)6) and FFY3/2dt (TOT3-(c-myc)3 TOT2-(HA)6) were probed with 3F10 (anti-HA) and Q5 to detect Tot1-HA, Tot2-HA, and phosphoforms (
) of Tot1 and Tot1-HA are shown by arrows. (B) Phosphorylation of Tot1 requires full-length protein. 9E10 (anti-c-Myc) immunoprecipitates from strains FFY3/1dt (TOT3-(c-myc)3 TOT1-(HA)6) and FFY3/2dt (TOT3-(c-myc)3 TOT2-(HA)6) were probed with 3F10 (anti-HA) and Q5 to detect Tot1-HA, Tot2-HA, and phosphoforms ( ) of Tot1 and Tot1-HA. The truncated (∼20 kDa) Tot1-HA form is indicated (*) (also see Figure 2B). (C) Phosphorylation of Tot1 is supported by Elongator partner protein Kti11. 9E10 (anti-c-Myc) immunoprecipitates from the strains FFY3/2dt (KTI11) and DJY3/2-d11 (kti11Δ) coexpressing epitope-tagged Tot2 and Tot3 were probed with anti-Elp1/Tot1, Q5 and Q7 antibodies. Truncated Tot1 is indicated (*). Numbers (A and B) refer to protein marker sizes in kilodaltons (Invitrogen).
) of Tot1 and Tot1-HA. The truncated (∼20 kDa) Tot1-HA form is indicated (*) (also see Figure 2B). (C) Phosphorylation of Tot1 is supported by Elongator partner protein Kti11. 9E10 (anti-c-Myc) immunoprecipitates from the strains FFY3/2dt (KTI11) and DJY3/2-d11 (kti11Δ) coexpressing epitope-tagged Tot2 and Tot3 were probed with anti-Elp1/Tot1, Q5 and Q7 antibodies. Truncated Tot1 is indicated (*). Numbers (A and B) refer to protein marker sizes in kilodaltons (Invitrogen).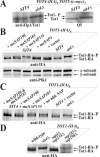
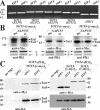
 ) forms are shown. sit4Δ cells accumulate the up-shifted Tot1-
) forms are shown. sit4Δ cells accumulate the up-shifted Tot1- form. (B) sit4Δ or multicopy SAP155 cells suppress Tot1 dephosphorylation. Protein extracts from strains DJY103 (sit4Δ TOT1-(HA)6), DJY102 (SIT4 TOT1-(HA)6), and DJY102 carrying the indicated multicopy SAP constellations were standardized by anti-Pfk1 (see Figure 2B) and probed with 3F10 (anti-HA). (C) Suppressed Tot1 dephosphorylation by multicopy SAP155 is antagonized by excess Sap185/190. Protein extracts from indicated TOT-(HA)6 expressors were probed with 3F10 (anti-HA) to monitor Tot1-HA migration dependent on SAP copy number. (D) sap185Δsap190Δ cells phenocopy high phospho-Tot1 levels of sit4Δ cells. Strains DJY102 (SIT4), DJY103 (sit4Δ), DJY115 (sap4Δsap155Δ), and DJY116 (sap185Δsap190Δ) expressing TOT1-(HA)6 were analyzed as described above (B and C). Non- and phosphorylated forms (
form. (B) sit4Δ or multicopy SAP155 cells suppress Tot1 dephosphorylation. Protein extracts from strains DJY103 (sit4Δ TOT1-(HA)6), DJY102 (SIT4 TOT1-(HA)6), and DJY102 carrying the indicated multicopy SAP constellations were standardized by anti-Pfk1 (see Figure 2B) and probed with 3F10 (anti-HA). (C) Suppressed Tot1 dephosphorylation by multicopy SAP155 is antagonized by excess Sap185/190. Protein extracts from indicated TOT-(HA)6 expressors were probed with 3F10 (anti-HA) to monitor Tot1-HA migration dependent on SAP copy number. (D) sap185Δsap190Δ cells phenocopy high phospho-Tot1 levels of sit4Δ cells. Strains DJY102 (SIT4), DJY103 (sit4Δ), DJY115 (sap4Δsap155Δ), and DJY116 (sap185Δsap190Δ) expressing TOT1-(HA)6 were analyzed as described above (B and C). Non- and phosphorylated forms ( ) of Tot1-HA (B-D) are shown by arrows; vector control (B and C) denotes empty YEp24 vector used to clone the SAP genes in multicopy (Luke et al., 1996).
) of Tot1-HA (B-D) are shown by arrows; vector control (B and C) denotes empty YEp24 vector used to clone the SAP genes in multicopy (Luke et al., 1996).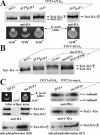
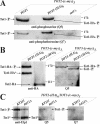
 ) Tot1-HA forms are shown. (B) Excess Tot4 shifts electrophoretic mobility of Tot1, a situation antagonized by excess Sit4·Sap190. Standardized protein extracts from strain DJY102 (SIT4 TOT4) expressing TOT1-(HA)6 and maintaining multicopy (mc) TOT4, SIT4, and SAP190 genes as indicated were probed with 3F10 (anti-HA). As a control served DJY104 (tot4Δ) (see A). (C) mcTOT4 intensifies Tot1 phosphorylation. 9E10 (anti-c-Myc) immunoprecipitates from strain FFY2/1dt (TOT1-(HA)6 TOT2-(c-myc)3) maintaining single copy or mcTOT4 were probed with 3F10 (anti-HA), 9E10 (antic-Myc), Q5 (anti-phosphoserine) and Q7 (anti-phosphothreonine) antibodies to detect Tot1-HA, Tot2-c-Myc and phospho-Tot1-HA (
) Tot1-HA forms are shown. (B) Excess Tot4 shifts electrophoretic mobility of Tot1, a situation antagonized by excess Sit4·Sap190. Standardized protein extracts from strain DJY102 (SIT4 TOT4) expressing TOT1-(HA)6 and maintaining multicopy (mc) TOT4, SIT4, and SAP190 genes as indicated were probed with 3F10 (anti-HA). As a control served DJY104 (tot4Δ) (see A). (C) mcTOT4 intensifies Tot1 phosphorylation. 9E10 (anti-c-Myc) immunoprecipitates from strain FFY2/1dt (TOT1-(HA)6 TOT2-(c-myc)3) maintaining single copy or mcTOT4 were probed with 3F10 (anti-HA), 9E10 (antic-Myc), Q5 (anti-phosphoserine) and Q7 (anti-phosphothreonine) antibodies to detect Tot1-HA, Tot2-c-Myc and phospho-Tot1-HA ( ). Before immunoprecipitation, extracts were standardized by anti-Pfk1 to follow content of Pfk1 α and β subunits (Figure 2B). Tot1-HA truncation is indicated (*). For zymocin read-outs (A and C), see Figure 1A.
). Before immunoprecipitation, extracts were standardized by anti-Pfk1 to follow content of Pfk1 α and β subunits (Figure 2B). Tot1-HA truncation is indicated (*). For zymocin read-outs (A and C), see Figure 1A.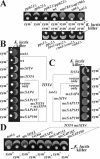

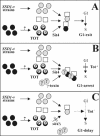
 ) and Sit4-dependent dephosphorylation of the toxin-target (TOT) substrate (
) and Sit4-dependent dephosphorylation of the toxin-target (TOT) substrate ( ) activate a key cell cycle regulator (□) required for processes preSTART. In the presence of γ-toxin (B), the critical protein can be sequestered and inactivated in combination with Sit4's dephosphorylated TOT substrate (•) to induce the G1 arrest (Tot+), irrespective of whether the alternative, Sit4-dispensable SSD1-v pathway would be sufficient. Failure to dephosphorylate TOT (C) no longer permits inactivation of the crucial regulator and causes sit4Δ cells to resist γ-toxicity (Tot-) at the expense of being G1 cell cycle delayed. The as yet elusive Elongator-specific kinase is marked by?.
) activate a key cell cycle regulator (□) required for processes preSTART. In the presence of γ-toxin (B), the critical protein can be sequestered and inactivated in combination with Sit4's dephosphorylated TOT substrate (•) to induce the G1 arrest (Tot+), irrespective of whether the alternative, Sit4-dispensable SSD1-v pathway would be sufficient. Failure to dephosphorylate TOT (C) no longer permits inactivation of the crucial regulator and causes sit4Δ cells to resist γ-toxicity (Tot-) at the expense of being G1 cell cycle delayed. The as yet elusive Elongator-specific kinase is marked by?.Similar articles
-
Molecular analysis of KTI12/TOT4, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene required for Kluyveromyces lactis zymocin action.Mol Microbiol. 2002 Feb;43(3):783-91. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.02794.x. Mol Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 11929532
-
Distinct subsets of Sit4 holophosphatases are required for inhibition of Saccharomyces cerevisiae growth by rapamycin and zymocin.Eukaryot Cell. 2009 Nov;8(11):1637-47. doi: 10.1128/EC.00205-09. Epub 2009 Sep 11. Eukaryot Cell. 2009. PMID: 19749176 Free PMC article.
-
Elongator function depends on antagonistic regulation by casein kinase Hrr25 and protein phosphatase Sit4.Mol Microbiol. 2009 Sep;73(5):869-81. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2009.06811.x. Epub 2009 Jul 28. Mol Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19656297
-
Structures and Activities of the Elongator Complex and Its Cofactors.Enzymes. 2017;41:117-149. doi: 10.1016/bs.enz.2017.03.001. Epub 2017 Apr 12. Enzymes. 2017. PMID: 28601220 Review.
-
Zymocin, a composite chitinase and tRNase killer toxin from yeast.Biochem Soc Trans. 2007 Dec;35(Pt 6):1533-7. doi: 10.1042/BST0351533. Biochem Soc Trans. 2007. PMID: 18031261 Review.
Cited by
-
The sensitivity of yeast mutants to oleic acid implicates the peroxisome and other processes in membrane function.Genetics. 2007 Jan;175(1):77-91. doi: 10.1534/genetics.106.064428. Epub 2006 Dec 6. Genetics. 2007. PMID: 17151231 Free PMC article.
-
The Snf1 protein kinase and Sit4 protein phosphatase have opposing functions in regulating TATA-binding protein association with the Saccharomyces cerevisiae INO1 promoter.Genetics. 2005 Apr;169(4):1957-72. doi: 10.1534/genetics.104.038075. Epub 2005 Feb 16. Genetics. 2005. PMID: 15716495 Free PMC article.
-
Yeast Elongator protein Elp1p does not undergo proteolytic processing in exponentially growing cells.Microbiologyopen. 2015 Dec;4(6):867-78. doi: 10.1002/mbo3.285. Epub 2015 Sep 25. Microbiologyopen. 2015. PMID: 26407534 Free PMC article.
-
Sulfur transfer and activation by ubiquitin-like modifier system Uba4•Urm1 link protein urmylation and tRNA thiolation in yeast.Microb Cell. 2016 Oct 24;3(11):554-564. doi: 10.15698/mic2016.11.539. Microb Cell. 2016. PMID: 28357324 Free PMC article.
-
tRNA binding to Kti12 is crucial for wobble uridine modification by Elongator.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Apr 10;53(7):gkaf296. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaf296. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 40226916 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arndt, K.T., Styles, C.A., and Fink, G.R. (1989). A suppressor of a HIS4 transcriptional defect encodes a protein with homology to the catalytic subunit of protein phosphatases. Cell 56, 527-537. - PubMed
-
- Berben, G., Dumont, J., Gilliquet, V., Bolle, P.A., and Hilger, F. (1991). The YDp plasmids: a uniform set of vectors bearing versatile gene disruption cassettes for Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 7, 475-477. - PubMed
-
- Bradford, M.M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72, 248-254. - PubMed
-
- Butler, A.R., O'Donnell, R.W., Martin, V.J., Gooday, G.W., and Stark, M.J. (1991a). Kluyveromyces lactis toxin has an essential chitinase activity. Eur. J. Biochem. 199, 483-488. - PubMed
-
- Butler, A.R., White, J.H., and Stark, M.J. (1991b). Analysis of the response of Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells to Kluyveromyces lactis toxin. J. Gen. Microbiol. 137, 1749-1757. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

