TOGp, the human homolog of XMAP215/Dis1, is required for centrosome integrity, spindle pole organization, and bipolar spindle assembly
- PMID: 14718566
- PMCID: PMC379257
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e03-07-0544
TOGp, the human homolog of XMAP215/Dis1, is required for centrosome integrity, spindle pole organization, and bipolar spindle assembly
Abstract
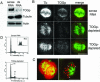
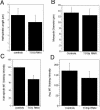
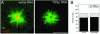
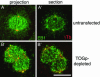
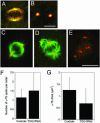
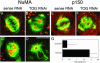
The XMAP215/Dis1 MAP family is thought to regulate microtubule plus-end assembly in part by antagonizing the catastrophe-promoting function of kin I kinesins, yet XMAP215/Dis1 proteins localize to centrosomes. We probed the mitotic function of TOGp (human homolog of XMAP215/Dis1) using siRNA. Cells lacking TOGp assembled multipolar spindles, confirming results of Gergely et al. (2003. Genes Dev. 17, 336-341). Eg5 motor activity was necessary to maintain the multipolar morphology. Depletion of TOGp decreased microtubule length and density in the spindle by approximately 20%. Depletion of MCAK, a kin I kinesin, increased MT lengths and density by approximately 20%, but did not disrupt spindle morphology. Mitotic cells lacking both TOGp and MCAK formed bipolar and monopolar spindles, indicating that TOGp and MCAK contribute to spindle bipolarity, without major effects on MT stability. TOGp localized to centrosomes in the absence of MTs and depletion of TOGp resulted in centrosome fragmentation. TOGp depletion also disrupted MT minus-end focus at the spindle poles, detected by localizations of NuMA and the p150 component of dynactin. The major functions of TOGp during mitosis are to focus MT minus ends at spindle poles, maintain centrosome integrity, and contribute to spindle bipolarity.
Figures


References
-
- Becker, B.E., Romney, S.J., and Gard, D.L. (2003). XMAP215, XKCM1, NuMA and cytoplasmic dynein are required for the assembly and organization of the transient microtubule array during maturation of Xenopus oocytes. Dev. Biol. 261, 488-505. - PubMed
-
- Bellanger, J.M., and Gonczy, P. (2003). TAC-1 and ZYG-9 form a complex that promotes microtubule assembly in C. elegans embryos. Curr Biol. 13, 1488-1498. - PubMed
-
- Bornens, M. (2002). Centrosome composition and microtubule anchoring mechanisms. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 14, 25-34. - PubMed
-
- Cassimeris, L., Gard, D., Tran, P.T., and Erickson, H.P. (2001). XMAP215 is a long thin molecule which does not increase microtubule stiffness. J. Cell Sci. 114, 3025-3033. - PubMed
-
- Charrasse, S., Schroeder, M., Gauthier-Rouviere, C., Ango, F., Cassimeris, L., Gard, D.L., and Larroque, C. (1998). The TOGp protein is a new human microtubule-associated protein homologous to the Xenopus XMAP215. J. Cell Sci. 111, 1371-1383. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

