Effects of mutations in the cytoplasmic domain of herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein B on intracellular transport and infectivity
- PMID: 14722308
- PMCID: PMC321396
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.78.3.1540-1551.2004
Effects of mutations in the cytoplasmic domain of herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein B on intracellular transport and infectivity
Abstract
Herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) is a human pathogen of the alphaherpesvirus family which infects and spreads in the nervous system. Glycoproteins play a key role in the process of assembly and maturation of herpesviruses, which is essential for neuroinvasion and transneuronal spread. Glycoprotein B (gB) is a main component of the HSV-1 envelope and is necessary for the production of infectious particles. The cytoplasmic domain of gB, the longest one among HSV-1 glycoproteins, contains several highly conserved peptide sequences homologous to motifs involved in intracellular sorting. To determine the specific roles of these motifs in processing, subcellular localization, and the capacity of HSV-1 gB to complement a gB-null virus, we generated truncated or point mutated forms of a green fluorescent protein (GFP)-tagged gB. GFP-gB with a deletion in the acidic cluster DGDADEDDL (amino acids [aa] 896 to 904) behaved the same as the parental form. Deletion or disruption of the YTQV motif (aa 889 to 892) abolished internalization and reduced complementation by 60%. Disruption of the LL motif (aa 871 to 872) impaired the return of the protein to the trans-Golgi network (TGN) while enhancing its recycling to the plasma membrane. Truncations from residue E 857 abolished transport and processing of the truncated proteins, which had null complementation activity, through the Golgi complex. Altogether, our results favor a model in which HSV-1 gets its final envelope in the TGN, and they suggest that endocytosis, albeit not necessary, might play a role in infectivity.
Figures

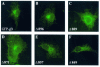


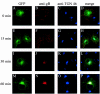




References
-
- Berlioz-Torrent, C., B. L. Shacklett, L. Erdtmann, L. Delamarre, I. Bouchaert, P. Sonigo, M. C. Dokhelar, and R. Benarous. 1999. Interactions of the cytoplasmic domains of human and simian retroviral transmembrane proteins with components of the clathrin adaptor complexes modulate intracellular and cell surface expression of envelope glycoproteins. J. Virol. 73:1350-1361. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bonneau, R. H., L. A. Salvucci, D. C. Johnson, and S. S. Tevethia. 1993. Epitope specificity of H-2Kb-restricted, HSV-1-, and HSV-2-cross-reactive cytotoxic T lymphocyte clones. Virology 195:62-70. - PubMed
-
- Brideau, A. D., L. W. Enquist, and R. S. Tirabassi. 2000. The role of virion membrane protein endocytosis in the herpesvirus life cycle. J. Clin. Virol. 17:69-82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

