Differential cytokine response in interstitial fluid in skin and serum during experimental inflammation in rats
- PMID: 14724215
- PMCID: PMC1664888
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.057216
Differential cytokine response in interstitial fluid in skin and serum during experimental inflammation in rats
Abstract
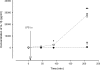
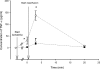
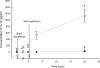
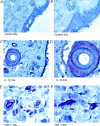
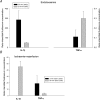
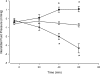
Tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta) are important mediators produced during inflammation. We hypothesized that the pro-inflammatory cytokine response in the interstitial fluid (IF) is different from that in serum, and we aimed at quantifying the amount of TNF-alpha and IL-1beta in the IF. By centrifugation of rat skin at < 424 g pure IF is extracted. Using ELISA such fluid was analysed for cytokines in back and/or paw skin of pentobarbital-anaesthetized rats, after either induction of endotoxaemia or ischaemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury. During endotoxaemia, TNF-alpha increased in the IF from 0 in control to 640 +/- 100 pg ml(-1) (mean +/-s.e.m.) after 90 min, with the serum concentration being 5-10 times higher at all time points. The response pattern of IL-1beta after lipopolysaccharide (LPS) challenge differed greatly from that of TNF-alpha with a large increase in IF from 390 +/- 90 to 28 000 +/- 1500 pg ml(-1) after 210 min, and a significantly smaller increase in serum (600 +/- 45 pg ml(-1)). During reperfusion of the hind paw after 2 h of ischaemia, there was a gradual increase of TNF-alpha in both IF of the paw skin and serum after 3 min of reperfusion. Both declined after 20 min. The pattern for IL-1beta differed, increasing significantly less in serum (25 +/- 15 pg ml(-1) after 20 min of reperfusion) than in the IF (1100 +/- 200 pg ml(-1)). Immunostaining of the inflamed tissues showed increased expression of the two cytokines in cells of both epidermis and dermis compared to controls. Subdermal injections of TNF-alpha and IL-1beta at the same concentrations found in IF after LPS infusion affected interstitial fluid pressure significantly. Local TNF-alpha production dominates after I/R injury, whereas in endotoxaemia systemic production predominates. For IL-1beta local production dominates in both conditions. Thus, there is a differential pattern of cytokine production and the current method allows the study of the role of cytokines in IF during different inflammatory reactions.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A novel function of insulin in rat dermis.J Physiol. 2004 Sep 1;559(Pt 2):583-91. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.067751. Epub 2004 Jul 2. J Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15235083 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation of rat trachea interstitial fluid and demonstration of local cytokine production in lipopolysaccharide-induced systemic inflammation.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2008 Mar;104(3):809-20. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00846.2007. Epub 2008 Jan 10. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2008. PMID: 18187613
-
Mast cell activation and its relation to proinflammatory cytokine production in the rheumatoid lesion.Arthritis Res. 2000;2(1):65-74. doi: 10.1186/ar70. Arthritis Res. 2000. PMID: 11219391 Free PMC article.
-
Potential of anticytokine therapies in central nervous system ischaemia.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2001 Mar;1(2):227-37. doi: 10.1517/14712598.1.2.227. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2001. PMID: 11727532 Review.
-
Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha: Ally and Enemy in Protean Cutaneous Sceneries.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 16;25(14):7762. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147762. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39063004 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Eugene M Renkin. His Many Contributions to Microvascular Research With Examples of How They Inform Current Investigations of Microvascular Dysfunction.Microcirculation. 2025 May;32(4):e70010. doi: 10.1111/micc.70010. Microcirculation. 2025. PMID: 40402867 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytokine signalling in rat pulp interstitial fluid and transcapillary fluid exchange during lipopolysaccharide-induced acute inflammation.J Physiol. 2006 May 15;573(Pt 1):225-36. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.104711. Epub 2006 Mar 9. J Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16527857 Free PMC article.
-
Opportunities and challenges in the diagnostic utility of dermal interstitial fluid.Nat Biomed Eng. 2023 Dec;7(12):1541-1555. doi: 10.1038/s41551-022-00998-9. Epub 2023 Jan 19. Nat Biomed Eng. 2023. PMID: 36658344 Review.
-
A novel function of insulin in rat dermis.J Physiol. 2004 Sep 1;559(Pt 2):583-91. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.067751. Epub 2004 Jul 2. J Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15235083 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammatory Markers in Suction Blister Fluid: A Comparative Study Between Interstitial Fluid and Plasma.Front Immunol. 2020 Nov 3;11:597632. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.597632. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33224151 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aukland K. Distribution volumes and macromolecular mobility in rat tail tendon interstitium. Am J Physiol. 1991;260:H409–H419. - PubMed
-
- Aukland K, Reed RK. Interstitial-lymphatic mechanisms in the control of extracellular fluid volume. Physiol Rev. 1993;73:1–78. - PubMed
-
- Beutler B, Milsark IW, Cerami AC. Passive immunization against cachectin/tumor necrosis factor protects mice from lethal effect of endotoxin. Science. 1985;229:869–871. - PubMed
-
- Dinarello CA. ELISA kits based on monoclonal antibodies do not measure total IL-1 beta synthesis. J Immunol Meth. 1992;148:255–259. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

