Attenuated response to stress and novelty and hypersensitivity to seizures in 5-HT4 receptor knock-out mice
- PMID: 14724239
- PMCID: PMC6729986
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2806-03.2004
Attenuated response to stress and novelty and hypersensitivity to seizures in 5-HT4 receptor knock-out mice
Abstract
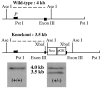
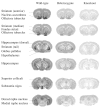
To study the functions of 5-HT4 receptors, a null mutation was engineered in the corresponding gene. 5-HT4 receptor knock-out mice displayed normal feeding and motor behaviors in baseline conditions but abnormal feeding and locomotor behavior in response to stress and novelty. Specifically, stress-induced hypophagia and novelty-induced exploratory activity were attenuated in the knock-out mice. In addition, pentylenetetrazol-induced convulsive responses were enhanced in the knock-out mice, suggesting an increase in neuronal network excitability. These results provide the first example of a genetic deficit that disrupts the ability of stress to reduce feeding and body weight and suggest that 5-HT4 receptors may be involved in stress-induced anorexia and seizure susceptibility.
Figures





References
-
- Beck B (2000) Neuropeptides and obesity. Nutrition 16: 916-923. - PubMed
-
- Bijak M, Misgeld U (1997) Effects of serotonin through serotonin1A and serotonin4 receptors on inhibition in the guinea-pig dentate gyrus in vitro Neuroscience 78: 1017-1026. - PubMed
-
- Bockaert J, Sebben M, Dumuis A (1990) Pharmacological characterization of 5-HT4 receptors positively coupled to adenylate cyclase in adult guinea pig hippocampal membranes: effect of substituted benzamide derivatives. Mol Pharmacol 37: 408-411. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
