The C. elegans microRNA let-7 binds to imperfect let-7 complementary sites from the lin-41 3'UTR
- PMID: 14729570
- PMCID: PMC324419
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1165404
The C. elegans microRNA let-7 binds to imperfect let-7 complementary sites from the lin-41 3'UTR
Abstract
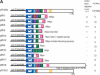
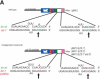
Caenorhabditis elegans let-7, a founding member of the microRNA family, is predicted to bind to six sites in the 3'UTR of the mRNA of its target gene, lin-41, to down-regulate LIN-41. Here, we demonstrate that wild-type let-7 microRNA binds in vitro to RNA from the lin-41 3'UTR. This interaction is dependent on two conserved let-7 complementary sites (LCSs). A 27-nucleotide sequence between the LCSs is also necessary for down-regulation in vivo. LCS mutations compensatory to the lesion in let-7(n2853) can partially restore lin-41 3'UTR function in a let-7(n2853) background, providing the first experimental evidence for an animal miRNA binding directly to its validated target in vivo.
Figures





References
-
- Bernstein E., Caudy, A.A., Hammond, S.M., and Hannon, G.J. 2001. Role for bidentate ribonuclease in the initiation step of RNA interference. Nature 409: 295-296. - PubMed
-
- Brennecke J., Hipfner, D.R., Stark, A., Russell, R.B., and Cohen, S.M. 2003. bantam encodes a developmentally regulated microRNA that controls cell proliferation and regulates the proapoptotic gene hid in Drosophila. Cell 113: 25-36. - PubMed
-
- Calin G.A., Dumitru, C.D., Shimizu, M., Bichi, R., Zupo, S., Noch, E., Aldler, H., Rattan, S., Keating, M., Rai, K., et al. 2002. Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro-RNA genes miR15 and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 99: 15524-15529. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
