A novel evolutionary lineage of carbonic anhydrase (epsilon class) is a component of the carboxysome shell
- PMID: 14729686
- PMCID: PMC321498
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.186.3.623-630.2004
A novel evolutionary lineage of carbonic anhydrase (epsilon class) is a component of the carboxysome shell
Abstract
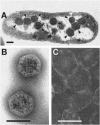
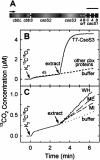
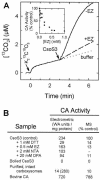
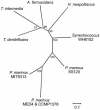
A significant portion of the total carbon fixed in the biosphere is attributed to the autotrophic metabolism of prokaryotes. In cyanobacteria and many chemolithoautotrophic bacteria, CO(2) fixation is catalyzed by ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (RuBisCO), most if not all of which is packaged in protein microcompartments called carboxysomes. These structures play an integral role in a cellular CO(2)-concentrating mechanism and are essential components for autotrophic growth. Here we report that the carboxysomal shell protein, CsoS3, from Halothiobacillus neapolitanus is a novel carbonic anhydrase (epsilon-class CA) that has an evolutionary lineage distinct from those previously recognized in animals, plants, and other prokaryotes. Functional CAs encoded by csoS3 homologues were also identified in the cyanobacteria Prochlorococcus sp. and Synechococcus sp., which dominate the oligotrophic oceans and are major contributors to primary productivity. The location of the carboxysomal CA in the shell suggests that it could supply the active sites of RuBisCO in the carboxysome with the high concentrations of CO(2) necessary for optimal RuBisCO activity and efficient carbon fixation in these prokaryotes, which are important contributors to the global carbon cycle.
Figures



References
-
- Badger, M. R., D. Hanson, and G. D. Price. 2002. Evolution and diversity of CO2 concentrating mechanisms in cyanobacteria. Funct. Plant Biol. 29:161-173. - PubMed
-
- Baker, S. H., S. Jin, H. C. Aldrich, G. T. Howard, and J. M. Shively. 1998. Insertion mutation of the form I cbbL gene encoding ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (RuBisCO) in Thiobacillus neapolitanus results in expression of form II RuBisCO, loss of carboxysomes, and an increased CO2 requirement for growth. J. Bacteriol. 180:4133-4139. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baker, S. H., S. C. Lorbach, M. Rodriguez-Buey, D. S. Williams, H. C. Aldrich, and J. M. Shively. 1999. The correlation of the gene csoS2 of the carboxysome operon with two polypeptides of the carboxysome in Thiobacillus neapolitanus. Arch. Microbiol. 172:233-239. - PubMed
-
- Baker, S. H., D. S. Williams, H. C. Aldrich, A. C. Gambrell, and J. M. Shively. 2000. Identification and localization of the carboxysome peptide Csos3 and its corresponding gene in Thiobacillus neapolitanus. Arch. Microbiol. 173:278-283. - PubMed
-
- Beudeker, R. F., G. C. Cannon, J. G. Kuenen, and J. M. Shively. 1980. Relations between d-ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase, carboxysomes, and CO2 fixing capacity in the obligate chemolithotroph Thiobacillus neapolitanus grown under different limitations in the chemostat. Arch. Microbiol. 124:185-189.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

