Physical and functional interactions of the Arf tumor suppressor protein with nucleophosmin/B23
- PMID: 14729947
- PMCID: PMC321449
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.24.3.985-996.2004
Physical and functional interactions of the Arf tumor suppressor protein with nucleophosmin/B23
Abstract
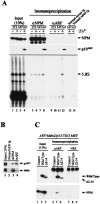
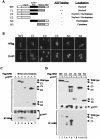
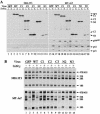
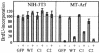
The Arf tumor suppressor inhibits cell cycle progression through both p53-dependent and p53-independent mechanisms, including interference with rRNA processing. Using tandem-affinity-tagged p19(Arf), we purified Arf-associated proteins from mouse NIH 3T3 fibroblasts undergoing cell cycle arrest. Tagged p19(Arf) associated with nucleolar and ribosomal proteins, including nucleophosmin/B23 (NPM), a protein thought to foster the maturation of preribosomal particles. NPM is an abundant protein, only a minor fraction of which binds to p19(Arf); however, a significant proportion of p19(Arf) associates with NPM. The interaction between p19(Arf) and NPM requires amino acid sequences at the Arf amino terminus, which are also required for Mdm2 binding, as well as the central acidic domain of NPM and an adjacent segment that regulates NPM oligomerization. The interaction between p19(Arf) and NPM occurs in primary mouse embryonic fibroblasts, including those lacking both Mdm2 and p53. In an NIH 3T3 derivative cell line (MT-Arf) engineered to conditionally express an Arf transgene, induced p19(Arf) associates with NPM and colocalizes with it in high-molecular-weight complexes (2 to 5 MDa). An NPM mutant lacking its carboxyl-terminal nucleic acid-binding domain oligomerizes with endogenous NPM, inhibits p19(Arf) from entering into 2- to 5-MDa particles, and overrides the ability of p19(Arf) to retard rRNA processing.
Figures



References
-
- Bassler, J., P. Grandi, O. Gadal, T. Leβmann, E. Petfalski, D. Tollervey, J. Lechner, and E. Hurt. 2001. Identification of a 60S preribosomal particle that is closely linked to nuclear export. Mol. Cell 8:517-529. - PubMed
-
- Carnero, A., J. D. Hudson, C. M. Price, and D. H. Beach. 2000. p16INK4A and p19ARF act in overlapping pathways in cellular immortalization. Nat. Cell Biol. 2:148-155. - PubMed
-
- Colombo, E., J.-C. Marine, D. Danovi, B. Falini, and P. G. Pelicci. 2002. Nucleophosmin regulates the stability and transcriptional activity of p53. Nat. Cell Biol. 4:529-533. - PubMed
-
- Dumbar, T. S., G. A. Gentry, and M. O. Olson. 1989. Interaction of nucleolar phosphoprotein B23 with nucleic acids. Biochemistry 28:9495-9501. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
