Mitochondrial proteins and complexes in Leishmania and Trypanosoma involved in U-insertion/deletion RNA editing
- PMID: 14730014
- PMCID: PMC1370527
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.5170704
Mitochondrial proteins and complexes in Leishmania and Trypanosoma involved in U-insertion/deletion RNA editing
Abstract
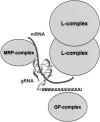
A number of mitochondrial proteins have been identified in Leishmania sp. and Trypanosoma brucei that may be involved in U-insertion/deletion RNA editing. Only a few of these have yet been characterized sufficiently to be able to assign functional names for the proteins in both species, and most have been denoted by a variety of species-specific and laboratory-specific operational names, leading to a terminology confusion both within and outside of this field. In this review, we summarize the present status of our knowledge of the orthologous and unique putative editing proteins in both species and the functional motifs identified by sequence analysis and by experimentation. An online Supplemental sequence database (http://164.67.60.200/proteins/protsmini1.asp) is also provided as a research resource.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Functional complementation of Trypanosoma brucei RNA in vitro editing with recombinant RNA ligase.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Mar 29;102(13):4712-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0500553102. Epub 2005 Mar 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15781861 Free PMC article.
-
A deletion site editing endonuclease in Trypanosoma brucei.Mol Cell. 2005 Nov 11;20(3):403-12. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2005.09.016. Mol Cell. 2005. PMID: 16285922
-
Isolation of a U-insertion/deletion editing complex from Leishmania tarentolae mitochondria.EMBO J. 2003 Feb 17;22(4):913-24. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg083. EMBO J. 2003. PMID: 12574127 Free PMC article.
-
Uridine insertion/deletion RNA editing in trypanosome mitochondria: a complex business.RNA. 2003 Mar;9(3):265-76. doi: 10.1261/rna.2178403. RNA. 2003. PMID: 12591999 Free PMC article. Review.
-
mRNA processing in the Trypanosomatidae.Experientia. 1991 Feb 15;47(2):118-28. doi: 10.1007/BF01945412. Experientia. 1991. PMID: 2001714 Review.
Cited by
-
Dual core processing: MRB1 is an emerging kinetoplast RNA editing complex.Trends Parasitol. 2013 Feb;29(2):91-9. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2012.11.005. Epub 2013 Jan 8. Trends Parasitol. 2013. PMID: 23305619 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multifunctional G-rich and RRM-containing domains of TbRGG2 perform separate yet essential functions in trypanosome RNA editing.Eukaryot Cell. 2012 Sep;11(9):1119-31. doi: 10.1128/EC.00175-12. Epub 2012 Jul 13. Eukaryot Cell. 2012. PMID: 22798390 Free PMC article.
-
OB-fold domain of KREPA4 mediates high-affinity interaction with guide RNA and possesses annealing activity.RNA. 2010 Oct;16(10):1951-67. doi: 10.1261/rna.2124610. Epub 2010 Aug 16. RNA. 2010. PMID: 20713467 Free PMC article.
-
Minimal pre-mRNA substrates with natural and converted sites for full-round U insertion and U deletion RNA editing in trypanosomes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2005 Nov 23;33(20):6610-20. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki943. Print 2005. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005. PMID: 16306234 Free PMC article.
-
Uridine insertion/deletion editing in trypanosomes: a playground for RNA-guided information transfer.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011 Sep-Oct;2(5):669-85. doi: 10.1002/wrna.82. Epub 2011 Mar 23. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011. PMID: 21823228 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aphasizhev, R. and Simpson, L. 2001. Isolation and characterization of a U-specific 3′–5′ exonuclease from mitochondria of Leishmania tarentolae. J. Biol. Chem. 276: 21280–21284. - PubMed
-
- Aphasizhev, R., Sbicego, S., Peris, M., Jang, S.H., Aphasizheva, I., Simpson, A.M., Rivlin, A., and Simpson, L. 2002. Trypanosome mitochondrial 3′ terminal uridylyl transferase (TUTase): The key enzyme in U-insertion/deletion RNA editing. Cell 108: 637–648. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
