Not all pseudouridine synthases are potently inhibited by RNA containing 5-fluorouridine
- PMID: 14730018
- PMCID: PMC1370531
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.5100104
Not all pseudouridine synthases are potently inhibited by RNA containing 5-fluorouridine
Abstract
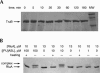
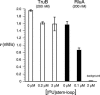
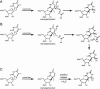
RNA containing 5-fluorouridine has been assumed to inhibit strongly or irreversibly the pseudouridine synthases that act on the RNA. RNA transcripts containing 5-fluorouridine in place of uridine have, therefore, been added to reconstituted systems in order to investigate the importance of particular pseudouridine residues in a given RNA by inactivating the pseudouridine synthase responsible for their generation. In sharp contradiction to the assumption of universal inhibition of pseudouridine synthases by RNA containing 5-fluorouridine, the Escherichia coli pseudouridine synthase TruB, which has physiologically critical eukaryotic homologs, is not inhibited by such RNA. Instead, the RNA containing 5-fluorouridine was handled as a substrate by TruB. The E. coli pseudouridine synthase RluA, on the other hand, forms a covalent complex and is inhibited stoichiometrically by RNA containing 5-fluorouridine. We offer a hypothesis for this disparate behavior and urge caution in interpreting results from reconstitution experiments in which RNA containing 5-fluorouridine is assumed to inhibit a pseudouridine synthase, as normal function may result from a failure to inactivate the targeted enzyme rather than from the absence of nonessential pseudouridine residues.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The pseudouridine synthases: revisiting a mechanism that seemed settled.J Am Chem Soc. 2004 Oct 13;126(40):12758-9. doi: 10.1021/ja046375s. J Am Chem Soc. 2004. PMID: 15469254
-
Mechanistic investigations of the pseudouridine synthase RluA using RNA containing 5-fluorouridine.Biochemistry. 2006 Oct 3;45(39):12029-38. doi: 10.1021/bi061293x. Biochemistry. 2006. PMID: 17002302 Free PMC article.
-
Unexpected linear ion trap collision-induced dissociation and Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance infrared multi-photon dissociation fragmentation of a hydrated C-glycoside of 5-fluorouridine formed by the action of the pseudouridine synthases RluA and TruB.Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2011 Sep 30;25(18):2627-32. doi: 10.1002/rcm.5162. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2011. PMID: 23657957 Free PMC article.
-
The roles of the essential Asp-48 and highly conserved His-43 elucidated by the pH dependence of the pseudouridine synthase TruB.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2005 Jan 1;433(1):322-34. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2004.09.009. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2005. PMID: 15581587 Review.
-
Pseudouridine synthases.Chem Biol. 2006 Nov;13(11):1125-35. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2006.09.009. Chem Biol. 2006. PMID: 17113994 Review.
Cited by
-
The handling of the mechanistic probe 5-fluorouridine by the pseudouridine synthase TruA and its consistency with the handling of the same probe by the pseudouridine synthases TruB and RluA.Biochemistry. 2011 Jan 25;50(3):426-36. doi: 10.1021/bi101737z. Epub 2010 Dec 29. Biochemistry. 2011. PMID: 21142053 Free PMC article.
-
Chemistry of Fluorinated Pyrimidines in the Era of Personalized Medicine.Molecules. 2020 Jul 29;25(15):3438. doi: 10.3390/molecules25153438. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32751071 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Formation of a stalled early intermediate of pseudouridine synthesis monitored by real-time FRET.RNA. 2010 Mar;16(3):610-20. doi: 10.1261/rna.1832510. Epub 2010 Jan 27. RNA. 2010. PMID: 20106954 Free PMC article.
-
Dye label interference with RNA modification reveals 5-fluorouridine as non-covalent inhibitor.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Nov 10;42(20):12735-45. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku908. Epub 2014 Oct 9. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 25300485 Free PMC article.
-
Detecting RNA modifications in the epitranscriptome: predict and validate.Nat Rev Genet. 2017 May;18(5):275-291. doi: 10.1038/nrg.2016.169. Epub 2017 Feb 20. Nat Rev Genet. 2017. PMID: 28216634 Review.
References
-
- Buck, M., Connick, M., and Ames, B.N. 1983. Complete analysis of tRNA modified nucleosides by high-performance liquid chromatography: The 29 modified nucleosides of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli tRNA. Anal. Biochem. 129: 1–13. - PubMed
-
- Collier, A.K., Arnold, J.R.P., and Fisher, J. 1996. NMR investigations of fluorine-labelled RNA: Application of two-dimensional heteronuclear experiments to study single-strand conformation. Magn. Reson. Chem. 34: 191–196.
-
- Foster, P.G., Huang, L., Santi, D.V., and Stroud, R.M. 2000. The structural basis for tRNA recognition and pseudouridine formation by pseudouridine synthase I. Nat. Struct. Biol. 7: 23–27. - PubMed
-
- Gehrke, C.W., Kuo, K.C., McCune, R.A., Gerhardt, K.O., and Agris, P.F. 1982. Quantitative enzymatic hydrolysis of tRNAs: Reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography of tRNA nucleosides. J. Chromatogr. 230: 297–308. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
