Characterization and functional identification of a novel plant 4,5-extradiol dioxygenase involved in betalain pigment biosynthesis in Portulaca grandiflora
- PMID: 14730069
- PMCID: PMC316306
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.103.031914
Characterization and functional identification of a novel plant 4,5-extradiol dioxygenase involved in betalain pigment biosynthesis in Portulaca grandiflora
Abstract
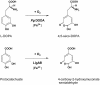
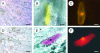
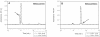
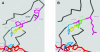
Betalains are pigments that replace anthocyanins in the majority of families of the plant order Caryophyllales. Betalamic acid is the common chromophore of betalains. The key enzyme of the betalain biosynthetic pathway is an extradiol dioxygenase that opens the cyclic ring of dihydroxy-phenylalanine (DOPA) between carbons 4 and 5, thus producing an unstable seco-DOPA that rearranges nonenzymatically to betalamic acid. A gene for a 4,5-DOPA-dioxygenase has already been isolated from the fungus Amanita muscaria, but no homolog was ever found in plants. To identify the plant gene, we constructed subtractive libraries between different colored phenotypes of isogenic lines of Portulaca grandiflora (Portulacaceae) and between different stages of flower bud formation. Using in silico analysis of differentially expressed cDNAs, we identified a candidate showing strong homology at the level of translated protein with the LigB domain present in several bacterial extradiol 4,5-dioxygenases. The gene was expressed only in colored flower petals. The function of this gene in the betalain biosynthetic pathway was confirmed by biolistic genetic complementation in white petals of P. grandiflora genotypes lacking the gene for color formation. This gene named DODA is the first characterized member of a novel family of plant dioxygenases phylogenetically distinct from Amanita sp. DOPA-dioxygenase. Homologs of DODA are present not only in betalain-producing plants but also, albeit with some changes near the catalytic site, in other angiosperms and in the bryophyte Physcomitrella patens. These homologs are part of a novel conserved plant gene family probably involved in aromatic compound metabolism.
Figures
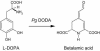




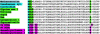
References
-
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic Local Alignment Search Tool. J Mol Biol 215: 403-410 - PubMed
-
- Ashton NW, Cove DJ, Featherstone DR (1979) Isolation and physiological analysis of mutants of the moss, Physcomitrella patens, which over-produce gametophores. Planta 144: 437-442 - PubMed
-
- Boyington JC, Gaffney BJ, Amzel LM (1993) The 3-dimensional structure of an arachidonic-acid 15-lipoxygenase. Science 260: 1482-1486 - PubMed
-
- Bradford MM (1976) Rapid and sensitive method for quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72: 248-254 - PubMed
-
- Clement JS, Mabry TJ (1996) Pigment evolution in the Caryophyllales: a systematic overview. Bot Acta 109: 360-367
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

