Effects of Cool-Water Immersion and High-Voltage Electric Stimulation for 3 Continuous Hours on Acute Edema in Rats
- PMID: 14737215
- PMCID: PMC314392
Effects of Cool-Water Immersion and High-Voltage Electric Stimulation for 3 Continuous Hours on Acute Edema in Rats
Abstract
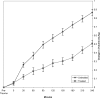
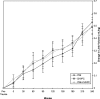
OBJECTIVE: Cool-water immersion (CWI) at 12.8 degrees C (55 degrees F), cathodal high-voltage pulsed current (CHVPC) at 120 pulses per second and 90% of visible motor threshold, or the combination of CWI and CHVPC, applied 30 minutes on, 30 minutes off for 4 hours, are known to curb edema formation after blunt trauma to the hind limbs of rats. Our purpose was to examine the effects of extending treatment times to 3 continuous hours after blunt trauma to the hind limbs of rats. DESIGN AND SETTING: A randomized, parallel-groups design of 22 subjects was used. Volumes of traumatized limbs, randomly assigned to CWI (n = 7), CHVPC (n = 8), or CWI followed by CHVPC (n = 7) were compared with those of injured but untreated limbs with analysis of variance. SUBJECTS: Twenty-two anesthetized Zucker lean rats (mass = 293 +/- 27 g). MEASUREMENTS: We measured limb volumes immediately before and after trauma and every 30 minutes over the 4-hour experiment. RESULTS: Volumes of treated limbs of all 3 experimental groups were smaller than those of untreated limbs (P <.05). No treatment was more effective than another. CONCLUSIONS: Exposure to either 3 hours of CWI or CHVPC or to 1 hour of CWI followed by 2 hours of CHVPC effectively curbed edema after blunt injury. These results suggest that these common treatments are effective only during application and hint that application should be maintained throughout the period during which edema is forming.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of Ibuprofen and High-Voltage Electric Stimulation on Acute Edema Formation After Blunt Trauma to Limbs of Rats.J Athl Train. 2005 Jun;40(2):111-115. J Athl Train. 2005. PMID: 15970957 Free PMC article.
-
Cool-Water Immersion and High-Voltage Electric Stimulation Curb Edema Formation in Rats.J Athl Train. 2003 Sep;38(3):225-230. J Athl Train. 2003. PMID: 14608432 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of cold water immersion on edema formation after blunt injury to the hind limbs of rats.J Athl Train. 1997 Jul;32(3):233-7. J Athl Train. 1997. PMID: 16558455 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of a single 30-minute treatment of high voltage pulsed current on edema formation in frog hind limbs.Phys Ther. 1992 Jan;72(1):63-8. doi: 10.1093/ptj/72.1.63. Phys Ther. 1992. PMID: 1728050
-
Influence of high voltage pulsed current on edema formation following impact injury in rats.Phys Ther. 1992 Sep;72(9):668-73. doi: 10.1093/ptj/72.9.668. Phys Ther. 1992. PMID: 1508974
Cited by
-
Effects of Ibuprofen and High-Voltage Electric Stimulation on Acute Edema Formation After Blunt Trauma to Limbs of Rats.J Athl Train. 2005 Jun;40(2):111-115. J Athl Train. 2005. PMID: 15970957 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Basur RL, Shephard E, Mouzas GL. A cooling method in the treatment of ankle sprains. Practitioner. 1976;216:708–711. - PubMed
-
- Cote DJ, Prentice WE, Jr, Hooker DN, Shields EW. Comparison of three treatment procedures for minimizing ankle sprain swelling. Phys Ther. 1988;68:1072–1076. - PubMed
-
- Hocutt JE, Jr, Jaffe R, Rylander CR, Beebe JK. Cryotherapy in ankle sprains. Am J Sports Med. 1982;10:316–319. - PubMed
-
- Knight KL. Cryotherapy in Sport Injury Management. Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics; 1995.
-
- Norwig JA. Injury management update: edema control and the acutely inverted ankle sprain. Athl Ther Today. 1997;2(1):40–41.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
