Phylogenetic and evolutionary analysis of the PLUNC gene family
- PMID: 14739326
- PMCID: PMC2286710
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.03332704
Phylogenetic and evolutionary analysis of the PLUNC gene family
Abstract
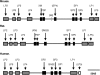
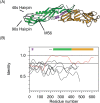
The PLUNC family of human proteins are candidate host defense proteins expressed in the upper airways. The family subdivides into short (SPLUNC) and long (LPLUNC) proteins, which contain domains predicted to be structurally similar to one or both of the domains of bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein (BPI), respectively. In this article we use analysis of the human, mouse, and rat genomes and other sequence data to examine the relationships between the PLUNC family proteins from humans and other species, and between these proteins and members of the BPI family. We show that PLUNC family clusters exist in the mouse and rat, with the most significant diversification in the locus occurring for the short PLUNC family proteins. Clear orthologous relationships are established for the majority of the proteins, and ambiguities are identified. Completion of the prediction of the LPLUNC4 proteins reveals that these proteins contain approximately a 150-residue insertion encoded by an additional exon. This insertion, which is predicted to be largely unstructured, replaces the structure homologous to the 40s hairpin of BPI. We show that the exon encoding this region is anomalously variable in size across the LPLUNC proteins, suggesting that this region is key to functional specificity. We further show that the mouse and human PLUNC family orthologs are evolving rapidly, which supports the hypothesis that these proteins are involved in host defense. Intriguingly, this rapid evolution between the human and mouse sequences is replaced by intense purifying selection in a large portion of the N-terminal domain of LPLUNC4. Our data provide a basis for future functional studies of this novel protein family.
Figures


References
-
- Andrault, J.-B., Gaillard, I., Giorgi, D., and Rouquier, S. 2003. Expansion of the BPI family by duplication on human chromosome 20: Characterization of the RY gene cluster in 20q11.21 encoding olfactory transporters/antimicrobial-like peptides. Genomics 82 172–184. - PubMed
-
- Beamer, L.J., Carroll, S.F., and Eisenberg, D. 1997. Crystal structure of human BPI and two bound phospholipids at 2.4 Å resolution. Science 276 1861–1864. - PubMed
-
- Bingle, C.D. and Bingle, L. 2000. Characterisation of the human plunc gene, a gene product with an upper airways and nasopharyngeal restricted expression pattern. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1493 363–367. - PubMed
-
- Bingle, C.D. and Craven, C.J. 2002. PLUNC: A novel family of candidate host defence proteins expressed in the upper airways and nasopharynx. Hum. Mol. Genet. 11 937–943. - PubMed
-
- Bruce, C., Beamer, L.J., and Tall, A.R. 1998. The implications of the structure of the bactericidal/permeability increasing protein on the lipid-transfer function of the cholesteryl ester transfer protein. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 8 426–434. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

