Escherichia coli YidC is a membrane insertase for Sec-independent proteins
- PMID: 14739936
- PMCID: PMC1271765
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600063
Escherichia coli YidC is a membrane insertase for Sec-independent proteins
Abstract
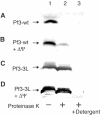
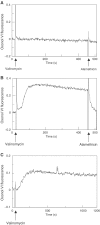
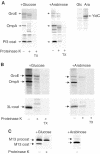
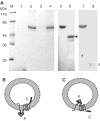
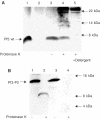
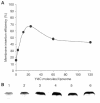
YidC is a recently discovered bacterial membrane protein that is related to the mitochondrial Oxa1p and the Alb3 protein of chloroplasts. These proteins are required in the membrane integration process of newly synthesized proteins that do not require the classical Sec machinery. Here we demonstrate that YidC is sufficient for the membrane integration of a Sec-independent protein. Microgram amounts of the purified single-spanning Pf3 coat protein were efficiently inserted into proteoliposomes containing the purified YidC. A mutant Pf3 coat protein with an extended hydrophobic region was inserted independently of YidC into the membrane both in vivo and in vitro, but its insertion was accelerated by YidC. These results show that YidC can function separately from the Sec translocase to integrate membrane proteins into the lipid bilayer.
Figures

References
-
- Apell HJ, Bersch B (1987) Oxonol VI as an optical indicator for membrane potentials in lipid vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta 903: 480–494 - PubMed
-
- Bassilana M, Wickner W (1993) Purified Escherichia coli preprotein translocase catalyzes multiple cycles of precursor protein translocation. Biochemistry 32: 2626–2630 - PubMed
-
- Brundage L, Hendrick JP, Schiebel E, Driessen AJM, Wickner W (1990) The purified E. coli integral membrane protein SecY/E is sufficient for reconstitution of SecA-dependent precursor protein translocation. Cell 62: 649–657 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

