Evidence of a novel quantitative-trait locus for obesity on chromosome 4p in Mexican Americans
- PMID: 14740316
- PMCID: PMC1181925
- DOI: 10.1086/381717
Evidence of a novel quantitative-trait locus for obesity on chromosome 4p in Mexican Americans
Erratum in
- Am J Hum Genet. 2004 May;74(5):1080
Abstract
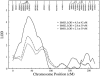
Although several genomewide scans have identified quantitative-trait loci influencing several obesity-related traits in humans, genes influencing normal variation in obesity phenotypes have not yet been identified. We therefore performed a genome scan of body mass index (BMI) on Mexican Americans, a population prone to obesity and diabetes, using a variance-components linkage analysis to identify loci that influence BMI. We used phenotypic data from 430 individuals (26% diabetics, 59% females, mean age +/- SD = 43 +/- 17 years, mean BMI +/- SD = 30.0 +/- 6.7, mean leptin (ng/ml) +/- SD = 22.1 +/- 17.1) distributed across 27 low-income Mexican American pedigrees who participated in the San Antonio Family Diabetes Study (SAFDS) for whom a 10-15-cM map is available. In this genomewide search, after accounting for the covariate effects of age, sex, diabetes, and leptin, we identified a genetic region exhibiting the most highly significant evidence for linkage (LOD 4.5) with BMI on chromosome 4p (4p15.1) at 42 cM, near marker D4S2912. This linkage result has been confirmed in an independent linkage study of severe obesity in Utah pedigrees. Two strong positional candidates, the human peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1 (PPARGC1) and cholecystokinin A receptor (CCKAR) with major roles in the development of obesity, are located in this region. In conclusion, we identified a major genetic locus influencing BMI on chromosome 4p in Mexican Americans.
Figures
References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- LocusLink, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/LocusLink/ (NCBI Build 33, assembled from Genbank genomic sequence data on April 28, 2003)
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for PPARGC1 and CCKAR)
References
-
- Adeyemo A, Luke A, Cooper R, Wu X, Tayo B, Zhu X, Rotimi C, Bouzekri N, Ward R (2003) A genome-wide scan for body mass index among Nigerian families. Obes Res 11:266–273 - PubMed
-
- Arya R, Blangero J, Almasy L, O’Connell P, Stern MP, Duggirala R (2001a) A major locus for body mass index (BMI) on chromosome 4p in Mexican Americans. Obes Res Suppl 9:70S
-
- Arya R, Duggirala R, Almasy L, Rainwater DL, Mahaney MC, Cole S, Dyer TD, Williams K, Leach RJ, Hixson JE, MacCluer JW, O’Connell P, Stern MP, Blangero J (2002) Linkage of high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol concentrations to a locus on chromosome 9p in Mexican Americans. Nat Genet 30:102–10510.1038/ng810 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical