Noradrenaline inhibits pacemaker currents through stimulation of beta 1-adrenoceptors in cultured interstitial cells of Cajal from murine small intestine
- PMID: 14744802
- PMCID: PMC1574247
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705665
Noradrenaline inhibits pacemaker currents through stimulation of beta 1-adrenoceptors in cultured interstitial cells of Cajal from murine small intestine
Abstract
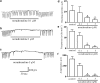
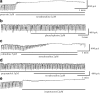
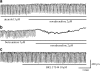
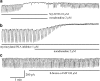
1. Interstitial cells of Cajal (ICCs) are pacemaker cells that activate the periodic spontaneous inward currents (pacemaker currents) responsible for the production of slow waves in gastrointestinal smooth muscle. The effects of noradrenaline on the pacemaker currents in cultured ICCs from murine small intestine were investigated by using whole-cell patch-clamp techniques at 30 degrees C. 2. Under current clamping, ICCs had a mean resting membrane potential of -58+/-5 mV and produced electrical slow waves. Under voltage clamping, ICCs produced pacemaker currents with a mean amplitude of -410+/-57 pA and a mean frequency of 16+/-2 cycles min(-1). 3. Under voltage clamping, noradrenaline inhibited the amplitude and frequency of pacemaker currents and increased resting currents in the outward direction in a dose-dependent manner. These effects were reduced by intracellular GDP beta S. 4. Noradrenaline-induced effects were blocked by propranolol (beta-adrenoceptor antagonist). However, neither prazosin (alpha(1)-adrenoceptor antagonist) nor yohimbine (alpha(2)-adrenoceptor antagonist) blocked the noradrenaline-induced effects. Phenylephrine (alpha(1)-adrenoceptor agonist) had no effect on the pacemaker currents, whereas isoprenaline (beta-adrenoceptor agonist) mimicked the effect of noradrenaline. Atenolol (beta(1)-adrenoceptor antagonist) blocked the noradrenaline-induced effects, but butoxamine (beta(2)-adrenoceptor antagonist) did not. In addition, BRL37344 (beta(3)-adrenoceptor agonist) had no effect on pacemaker currents. 5. 9-(Tetrahydro-2-furanyl)-9H-purine-6-amine (SQ-22536; adenylate cyclase inhibitor) and a myristoylated protein kinase A inhibitor did not inhibit the noradrenaline-induced effects and 8-bromo-cAMP had no effects on pacemaker currents. 8-Bromo-cGMP and SNAP inhibited pacemaker currents and these effects of SNAP were blocked by 1H-[1,2,4]oxadiazolo[4,3-a]quinoxalin-1-one (ODQ; a guanylate cyclase inhibitor). However, ODQ did not block the noradrenaline-induced effects. 6. Neither tetraethylammonium (a voltage-dependent K(+) channel blocker), apamin (a Ca(2+)-dependent K(+) channel blocker) nor glibenclamide (an ATP-sensitive K(+) channel blocker) blocked the noradrenaline-induced effects. 7. The results suggest that noradrenaline-induced stimulation of beta(1)-adrenoceptors in the ICCs inhibits pacemaker currents, and that this is mediated by the activation of G-protein. Neither adenylate cyclase, guanylate cyclase nor a K(+) channel-dependent pathway are involved in this effect of noradrenaline.
Figures


References
-
- AKIMOTO Y., HORINIUCHI T., TANAKA Y., KOIKE K. The beta2- and beta3-adrenoceptor-mediated relaxation induced by fenoterol in guinea pig taenia caecum. J. Smooth Muscle Res. 2002;38:145–151. - PubMed
-
- BAUER V. Inhibition of guinea-pig taenia-coli mediated by alpha-1-adrenoceptor, beta-2-adrenoceptor, and ATP-receptor activation. Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 1982;1:175–188.
-
- BÜLBRING E., TOMITA T. Catecholamine action on smooth muscle. Pharmacol. Rev. 1987;39:49–96. - PubMed
-
- DEMOL P., RUOFF H.J., WEITHRAUCH T.R. Rational pharmacotherapy of gastrointestinal motility disorders. Eur. J. Pediatr. 1989;148:489–495. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

