Histamine-induced inhibition of leukotriene biosynthesis in human neutrophils: involvement of the H2 receptor and cAMP
- PMID: 14744809
- PMCID: PMC1574237
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705654
Histamine-induced inhibition of leukotriene biosynthesis in human neutrophils: involvement of the H2 receptor and cAMP
Abstract
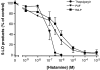
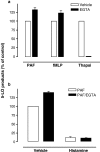
1. Histamine is generally regarded as a pro-inflammatory mediator in diseases such as allergy and asthma. A growing number of studies, however, suggest that this autacoid is also involved in the downregulation of human polymorphonuclear leukocyte (PMN) functions and inflammatory responses through activation of the Gs-coupled histamine H(2) receptor. 2. We report here that histamine inhibits thapsigargin- and ligand (PAF and fMLP)-induced leukotriene (LT) biosynthesis in human PMN in a dose-dependent manner. 3. The suppressive effect of histamine on LT biosynthesis was abrogated by the histamine H(2) receptor antagonists cimetidine, ranitidine, and tiotidine. In contrast, the histamine H(1), H(3), and H(4) receptor antagonists used in this study were ineffective in counteracting the inhibitory effect of histamine on the biosynthesis of LT in activated human PMN. 4. The inhibition of LT biosynthesis by histamine was characterized by decreased arachidonic acid release and 5-lipoxygenase translocation to the nuclear membrane. 5. Incubation of PMN with the cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) inhibitor N-[2-(p-bromocinnamylamino)ethyl]-5-isoquinoline-sulfonamide prevented the inhibitory effect of histamine on LT biosynthesis, suggesting an important role for PKA in this effect of histamine on LT biosynthesis in PMN. 6. These data provide the first evidences that, similarly to adenosine and prostaglandin E(2), histamine is a potent suppressor of LT biosynthesis, and support the concept that histamine may play a dual role in the regulation of inflammation.
Figures




References
-
- AMSELLEM C., CZARLEWSKI W., LAGARDE M., PACHECO Y. Inhibitory effect of loratadine on leukotriene B4 production by neutrophils either alone or during interaction with human airway epithelial cells. Pulmon. Pharmacol. Ther. 1998;11:245–252. - PubMed
-
- BAROODY F.M., NACLERIO R.M. Antiallergic effects of H1-receptor antagonists. Allergy. 2000;55:17–27. - PubMed
-
- BONVENTRE J.V., HUANG Z., TAHERI M.R., O'LEARY E., LI E., MOSKOWITZ M.A., SAPIRSTEIN A. Reduced fertility and postischaemic brain injury in mice deficient in cytosolic phospholipase A2. Nature. 1997;390:622–625. - PubMed
-
- BORGEAT P., PICARD S., DALLAIRE N., POULIOT M., SURETTE M.E.Quantitative studies of the lipid mediators of inflammation using liquid chromatography-electrospray mass spectrometry Molecular and Cellular Basis of Inflammation 1998Totowa, NJ: Humana Press Inc; 275–288.ed. Serhan C.N. & Ward, P.A. pp
-
- BORGEAT P., PICARD S., VALLERAND P., BOURGOIN S., ODEIMAT A., SIROIS P., POUBELLE P.E. Automated on-line extraction and profiling of lipoxygenase products of arachidonic acid by high-performance liquid chromatography. Methods Enzymol. 1990;187:98–116. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

