Liver transplantation for the treatment of moderately or well-differentiated hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 14745321
- PMCID: PMC1356206
- DOI: 10.1097/01.sla.0000109146.72827.76
Liver transplantation for the treatment of moderately or well-differentiated hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Objective: To determine the long-term results of liver transplantation for well- or moderately differentiated hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Summary background data: HCC patient selection for liver transplantation remains controversial, and deciding exclusively on the strength of criteria such as number and size of nodules appears prognostically inaccurate.
Methods: Since 1991, preoperative tumor grading has been used at our center to establish whether a patient with HCC is fit for transplantation. Poorly differentiated HCC cases were excluded, while size and number of nodules were not considered as absolute selection criteria. Thirty-three patients with moderately or well-differentiated HCC were prospectively studied after liver transplantation. A group of 15 patients with incidental HCC transplanted during the same period were also evaluated and compared with the 33 patients with preoperatively diagnosed HCC.
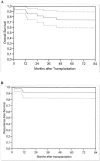
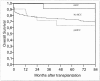
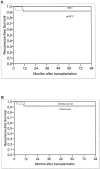
Results: On histologic examination, 38% of the entire group of 48 patients did not meet the "Milan criteria" and 42% were pTNM stages III and IV. The median follow-up was 44 months. The 5-year actuarial survival rate was 75% and recurrence-free survival was 92%. HCC recurred in only 3 patients (6%). The only histomorphologic variable differing significantly between incidental and nonincidental HCC was nodule size. The timing of diagnosis (incidental vs. nonincidental HCC), the Milan criteria, and the TNM stage revealed no statistically significant impact on overall and recurrence-free survival rates.
Conclusions: The routine pre-orthotopic liver transplantation tumor grading may represent a valid tool in the selection of unresectable HCC patients for transplantation.
Figures
Comment in
-
Liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: need for a new patient selection strategy.Ann Surg. 2004 Nov;240(5):923-4; author reply 924-5. doi: 10.1097/01.sla.0000143896.65218.e3. Ann Surg. 2004. PMID: 15492579 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Comment on
-
Challenging choices: liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma.Ann Surg. 2004 Feb;239(2):160-1. doi: 10.1097/01.sla.0000109169.72607.50. Ann Surg. 2004. PMID: 14745322 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Olthoff KM, Millis JM, Rosove MH, et al. Is liver transplantation justified for the treatment of hepatic malignancies? Arch Surg. 1990;125:1261–1268. - PubMed
-
- Llovet JM, Fuster J, Bruix J. Intention-to-treat analysis of surgical treatment for early hepatocellular carcinoma: resection versus transplantation. Hepatology. 1999;30:1434–1440. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

