Direct evidence that the VEGF-specific antibody bevacizumab has antivascular effects in human rectal cancer
- PMID: 14745444
- PMCID: PMC2693485
- DOI: 10.1038/nm988
Direct evidence that the VEGF-specific antibody bevacizumab has antivascular effects in human rectal cancer
Erratum in
- Nat Med. 2004 Jun;10(6):649
Abstract
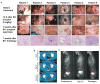
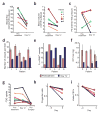
The effects of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) blockade on the vascular biology of human tumors are not known. Here we show here that a single infusion of the VEGF-specific antibody bevacizumab decreases tumor perfusion, vascular volume, microvascular density, interstitial fluid pressure and the number of viable, circulating endothelial and progenitor cells, and increases the fraction of vessels with pericyte coverage in rectal carcinoma patients. These data indicate that VEGF blockade has a direct and rapid antivascular effect in human tumors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
PET concerns in bevacizumab treatment.Nat Med. 2004 Jun;10(6):561; author reply 561. doi: 10.1038/nm0604-561a. Nat Med. 2004. PMID: 15170192 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

