Dynamics of pinned membranes with application to protein diffusion on the surface of red blood cells
- PMID: 14747313
- PMCID: PMC1303925
- DOI: 10.1016/S0006-3495(04)74153-3
Dynamics of pinned membranes with application to protein diffusion on the surface of red blood cells
Abstract
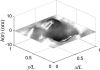
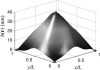
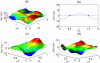
We present a theoretical treatment and simulation algorithm for the dynamics of Helfrich elastic membrane surfaces in the presence of general harmonic perturbations and hydrodynamic coupling to the surrounding solvent. In the limit of localized and strong interactions, this harmonic model can be used to pin the membrane to intracellular/intercellular structures. We consider the case of pinning to the cytoskeleton and use such a model to estimate the macroscopic diffusion constant for band 3 protein on the surface of human erythrocytes. Comparison to experimental results suggests that thermal undulations of the membrane surface should play a significant role in protein mobility on the red blood cell.
Figures

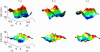




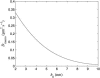
References
-
- Arfken, G. B., and H. J. Weber. 2001. Mathematical Methods for Physicists, 5th Ed. Academic Press, San Diego, CA. 90, 93.
-
- Ashcroft, N. W., and N. D. Mermin. 1976. Solid State Physics. Holt, Rinehart and Winston, New York.
-
- Atkins, P. W. 1990. Physical Chemistry, 4th ed. W. H. Freeman and Co., New York.
-
- Ayton, G., S. G. Bardenhagen, P. McMurty, D. Sulsky, and G. A. Voth. 2001. Interfacing continuum and molecular dynamics: an application to lipid bilayers. J. Chem. Phys. 114:6913–6924.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

