Clinical evaluation of the COBAS Amplicor HBV monitor test for measuring serum HBV DNA and comparison with the Quantiplex branched DNA signal amplification assay in Taiwan
- PMID: 14747437
- PMCID: PMC1770196
- DOI: 10.1136/jcp.2003.10835
Clinical evaluation of the COBAS Amplicor HBV monitor test for measuring serum HBV DNA and comparison with the Quantiplex branched DNA signal amplification assay in Taiwan
Abstract
Aims: To evaluate the performance characteristics and clinical usefulness of the COBAS Amplicor HBV monitor (COBAS-AM) test in Taiwan and to examine its correlation with the Quantiplex branched DNA signal amplification (bDNA) assay for measuring serum hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA concentrations.
Methods: HBV DNA was measured by the COBAS-AM test in 149 sera from chronic HBV infected patients that had previously been analysed by the bDNA assay.
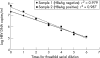
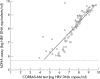
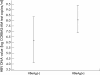
Results: The COBAS-AM test showed good reproducibility, with acceptable intra-assay and interassay coefficients of variation (1.6% and 0.9%, respectively) and good linearity (r2=0.98). The overall sensitivity of the COBAS-AM test was significantly higher than that of the bDNA assay (95.3% v 83.2%): 69.6% of samples with HBV DNA below the detection limit of the bDNA assay could be measured by the COBAS-AM test. There was a significant correlation between the results of the two assays (r=0.901; p<0.0001). On average, the results derived from the COBAS-AM test were 0.55 log lower than those of the bDNA assay. HBV DNA concentrations were significantly higher among HBV e antigen (HBeAg) positive patients than negative ones, and higher among patients with abnormal alanine aminotransferase (ALT) concentrations than those with normal ALT concentrations (p=0.0003).
Conclusions: The COBAS-AM assay, more sensitive in HBeAg negative samples than the bDNA assay, can effectively measure HBV DNA concentrations in Taiwanese patients. HBV DNA values measured by the COBAS-AM test and bDNA assay correlate significantly.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical evaluation of the digene hybrid capture II test and the COBAS AMPLICOR monitor test for determination of hepatitis B virus DNA levels.J Clin Microbiol. 2004 Aug;42(8):3513-7. doi: 10.1128/JCM.42.8.3513-3517.2004. J Clin Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15297491 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of clinical application of the Abbott HBV PCR kit and the VERSANT HBV DNA 3.0 test to measure serum hepatitis B virus DNA in Taiwanese patients.Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2009 Aug;25(8):413-22. doi: 10.1016/S1607-551X(09)70536-4. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2009. PMID: 19605335 Free PMC article.
-
Combined branched-DNA and conventional HBV PCR assays for detection of serum HBV-DNA in hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B patients.Hepatogastroenterology. 2006 Jan-Feb;53(67):106-9. Hepatogastroenterology. 2006. PMID: 16506386
-
Comparison of the nucleic acid-based crosslinking hybridization assay and the branched DNA signal amplification assay in the quantitative measurement of serum hepatitis B virus DNA.J Clin Lab Anal. 1999;13(6):296-300. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1098-2825(1999)13:6<296::aid-jcla8>3.0.co;2-c. J Clin Lab Anal. 1999. PMID: 10633298 Free PMC article.
-
Branched DNA signal amplification for direct quantitation of nucleic acid sequences in clinical specimens.Adv Clin Chem. 1998;33:201-35. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2423(08)60209-7. Adv Clin Chem. 1998. PMID: 10086178 Review.
Cited by
-
Factors contributing to antiviral effect of adefovir dipivoxil therapy added to ongoing lamivudine treatment in patients with lamivudine-resistant chronic hepatitis B.J Gastroenterol. 2009;44(6):601-7. doi: 10.1007/s00535-009-0038-6. Epub 2009 Apr 22. J Gastroenterol. 2009. PMID: 19387534
-
Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate in pregnancy for prevention of mother to child transmission of hepatitis B in a rural setting on the Thailand-Myanmar border: a cost-effectiveness analysis.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2021 Feb 22;21(1):157. doi: 10.1186/s12884-021-03612-z. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2021. PMID: 33618698 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic comparison between Daan real-time PCR and Cobas TaqMan for quantification of HBV DNA levels in patients with CHB.BMC Infect Dis. 2014 Feb 14;14:85. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-14-85. BMC Infect Dis. 2014. PMID: 24528480 Free PMC article.
-
A genetic variant of the NTCP gene is associated with HBV infection status in a Chinese population.BMC Cancer. 2016 Mar 12;16:211. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2257-6. BMC Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26968990 Free PMC article.
-
Rational design of DNA sequences for nanotechnology, microarrays and molecular computers using Eulerian graphs.Nucleic Acids Res. 2004 Aug 27;32(15):4630-45. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh802. Print 2004. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004. PMID: 15333695 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lee WM. Hepatitis B virus infection. N Engl J Med 1997;337:1733–45. - PubMed
-
- Chen DS. From hepatitis to hepatoma: lessons from type B viral hepatitis. Science 1993;262:369–70. - PubMed
-
- Stevens C, Beasley R, Tsui J, et al. Vertical transmission of hepatitis B antigen in Taiwan. N Engl J Med 1975;292:772–4. - PubMed
-
- Zhang YY, Hansson BG, Kuo LS, et al. Hepatitis B virus DNA in serum and liver is commonly found in Chinese patients with chronic liver disease despite the presence of antibodies to HBsAg. Hepatology 1993;17:538–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
