STAT-1: a novel regulator of apoptosis
- PMID: 14748743
- PMCID: PMC2517573
- DOI: 10.1111/j.0959-9673.2003.00363.x
STAT-1: a novel regulator of apoptosis
Abstract
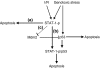
Extracellular signalling molecules binding to their specific receptors are able to modulate gene expression, leading to changes in development, cell growth and homeostasis. The signal transducers and activators of transcription (STAT) protein family members are among the best studied of the latent cytoplasmic signal-dependent transcription factors. The STAT factors are activated via phosphorylation on the C-terminal domain following cytokine signalling or by various stress-induced stimuli. Recently, STAT-1 has been implicated in modulating pro- and anti-apoptotic genes following several stress-induced responses. These effects are dependent on STAT-1 phosphorylation on serine-727 and require the C-terminal transactivation domain of STAT-1 to enhance its pro-apoptotic effect or inhibit its anti-apoptotic effects. The STAT-1 C-terminal domain has been demonstrated to be important for protein-protein interaction with other transcriptional activators. The reports that STAT-1-deficient mice develop spontaneous and chemically induced tumours more rapidly compared to wild-type mice and that STAT-1-deficient cells are more resistant to agents that induce apoptosis strongly support the argument that STAT-1 acts as a tumour suppressor.
Figures
References
-
- Battle TE, Frank DA. The role of STATs in apoptosis. Curr. Mol. Med. 2002;4:381–392. - PubMed
-
- Buhdram-Mahadeo VS, Morris PJ, Latchman DS. The Brn-3a transcription factor inhibits the pro-apoptotic effect of p53 and enhances cell cycle arrest by differentially regulating the activity of the p53 target genes encoding Bax and p21 (CIP1/Waf1) Oncogene. 2002;21:6123–6131. - PubMed
-
- Chung CD, Liao J, Liu B, et al. Specific inhibition of Stat3 signal transduction by PIAS3. Science. 1997;278:1803–1805. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

