The influence of diet upon liver function tests and serum lipids in healthy male volunteers resident in a Phase I unit
- PMID: 14748819
- PMCID: PMC1884438
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2125.2003.01969.x
The influence of diet upon liver function tests and serum lipids in healthy male volunteers resident in a Phase I unit
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the effect of diet upon liver function tests and serum lipids within the restricted environment of a Phase I unit.
Methods: An open randomized three-way crossover study was designed with subjects consuming three types of diet. The diets comprised, a balanced normal calorie diet, a high-carbohydrate high-calorie diet and a high-fat high-calorie diet. Each diet was consumed in a randomized sequence over 8 days with a recovery period of 14 days between periods. The blood concentrations of various laboratory parameters were measured at intervals throughout each dietary period and during the recovery periods.
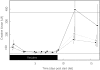
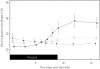
Results: Blood transaminase activity and triglyceride concentrations increased significantly whilst subjects consumed a high-carbohydrate high-calorie diet but not when fed either a high-fat high-calorie diet or a balanced normal calorie diet.
Conclusions: The rises in transaminases and triglycerides were caused by the carbohydrate content of the diet rather than its calorific value. Sucrose rather than starch was the carbohydrate which caused the rise in transaminases and triglycerides. The importance of controlling diet in Phase I studies is stressed.
Figures




References
-
- Stricker BHCH, Spoelstra P. Drug-induced hepatic injury. In: Dukes MNG, editor. Drug-induced disorders. Vol. 1. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 1985. pp. 1–10.
-
- Kanamaru M, Nagashima S, Uematsu T, Nakashima M. Influence of 7-day hospitalisation for Phase I study on the biochemical laboratory tests of healthy volunteers. Jpn J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1989;20:493–503.
-
- Kobayashi M, Yamada N, Shibata H, Nishikawa T. Elevation of serum transaminase value after administration of non-toxic drugs in some volunteers for Phase I trials: a study on the selection of volunteers. Jpn J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1991;22:497–500.
-
- Merz M, Seiberling M, Hoxter G, Holting M, Wortha HP. Elevation of liver enzymes in multiple dose trials during placebo treatment: are they predictable? J Clin Pharmacol. 1997;37:791–8. - PubMed
-
- Rosenzweig P, Brohier S, Zipfel A. Data on placebo in healthy volunteers: impact of experimental conditions on safety, and on laboratory and physiological variables during phase I trials. Therapie. 1996;51:356–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

