DJ-1 has a role in antioxidative stress to prevent cell death
- PMID: 14749723
- PMCID: PMC1298985
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400074
DJ-1 has a role in antioxidative stress to prevent cell death
Erratum in
- EMBO Rep. 2004 Apr;5(4):430
Abstract
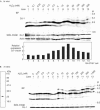
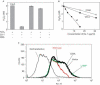
Deletion and point (L166P) mutations of DJ-1 have recently been shown to be responsible for the onset of familial Parkinson's disease (PD, PARK7). The aim of this study was to determine the role of DJ-1 in PD. We first found that DJ-1 eliminated hydrogen peroxide in vitro by oxidizing itself. We then found that DJ-1 knockdown by short interfering RNA rendered SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells susceptible to hydrogen peroxide-, MPP+- or 6-hydroxydopamine-induced cell death and that cells harbouring mutant forms of DJ-1, including L166P, became susceptible to death in parallel with the loss of oxidized forms of DJ-1. These results clearly showed that DJ-1 has a role in the antioxidative stress reaction and that mutations of DJ-1 lead to cell death, which is observed in PD.
Figures


References
-
- Bonifati V et al. (2003) Mutations in the DJ-1 gene associated with autosomal recessive early-onset Parkinsonism. Science 299: 256–259 - PubMed
-
- Heikkila R, Cohen G (1971) Inhibition of biogenic amine uptake by hydrogen peroxide: a mechanism for toxic effects of 6-hydroxydopamine. Science 172: 1257–1258 - PubMed
-
- Honbou K et al. (2003) The crystal structure of DJ-1, a protein related to male fertility and Parkinson's disease. J Biol Chem 278: 31380–31384 - PubMed
-
- Huai Q et al. (2003) Crystal structure of DJ-1/RS and implication on familial Parkinson's disease. FEBS Lett 549: 171–175 - PubMed
-
- Jacquot JP et al. (2002) Thioredoxins and related proteins in photosynthetic organisms: molecular basis for thiol dependent regulation. Biochem Pharmacol 64: 1065–1069 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

