A glycosylated type I membrane protein becomes cytosolic when peptide: N-glycanase is compromised
- PMID: 14749736
- PMCID: PMC1271816
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600090
A glycosylated type I membrane protein becomes cytosolic when peptide: N-glycanase is compromised
Abstract
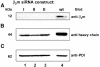
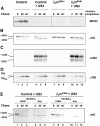
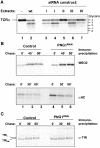
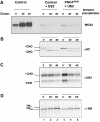
The human cytomegalovirus-encoded glycoprotein US2 catalyzes proteasomal degradation of Class I major histocompatibility complex (MHC) heavy chains (HCs) through dislocation of the latter from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to the cytosol. During this process, the Class I MHC HCs are deglycosylated by an N-glycanase-type activity. siRNA molecules designed to inhibit the expression of the light chain, beta(2)-microglobulin, block the dislocation of Class I MHC molecules, which implies that US2-dependent dislocation utilizes correctly folded Class I MHC molecules as a substrate. Here we demonstrate it is peptide: N-glycanase (PNGase or PNG1) that deglycosylates dislocated Class I MHC HCs. Reduction of PNGase activity by siRNA expression in US2-expressing cells inhibits deglycosylation of Class I MHC HC molecules. In PNGase siRNA-treated cells, glycosylated HCs appear in the cytosol, providing the first evidence for the presence of an intact N-linked type I membrane glycoprotein in the cytosol. N-glycanase activity is therefore not required for dislocation of glycosylated Class I MHC molecules from the ER.
Figures

References
-
- Bebok Z, Mazzochi C, King SA, Hong JS, Sorscher EJ (1998) The mechanism underlying cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator transport from the endoplasmic reticulum to the proteasome includes Sec61beta and a cytosolic, deglycosylated intermediary. J Biol Chem 273: 29873–29878 - PubMed
-
- Beckmann R, Spahn CM, Eswar N, Helmers J, Penczek PA, Sali A, Frank J, Blobel G (2001) Architecture of the protein-conducting channel associated with the translating 80S ribosome. Cell 107: 361–372 - PubMed
-
- Brodsky FM, Bodmer WF, Parham P (1979) Characterization of a monoclonal anti-beta 2-microglobulin antibody and its use in the genetic and biochemical analysis of major histocompatibility antigens. Eur J Immunol 9: 536–545 - PubMed
-
- Brummelkamp TR, Bernards R, Agami R (2002) Stable suppression of tumorigenicity by virus-mediated RNA interference. Cancer Cell 2: 243–247 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

