Genomewide scan in families with schizophrenia from the founder population of Afrikaners reveals evidence for linkage and uniparental disomy on chromosome 1
- PMID: 14750073
- PMCID: PMC1182255
- DOI: 10.1086/381713
Genomewide scan in families with schizophrenia from the founder population of Afrikaners reveals evidence for linkage and uniparental disomy on chromosome 1
Abstract
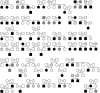
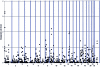
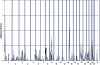
We report on our initial genetic linkage studies of schizophrenia in the genetically isolated population of the Afrikaners from South Africa. A 10-cM genomewide scan was performed on 143 small families, 34 of which were informative for linkage. Using both nonparametric and parametric linkage analyses, we obtained evidence for a small number of disease loci on chromosomes 1, 9, and 13. These results suggest that few genes of substantial effect exist for schizophrenia in the Afrikaner population, consistent with our previous genealogical tracing studies. The locus on chromosome 1 reached genomewide significance levels (nonparametric LOD score of 3.30 at marker D1S1612, corresponding to an empirical P value of.012) and represents a novel susceptibility locus for schizophrenia. In addition to providing evidence for linkage for chromosome 1, we also identified a proband with a uniparental disomy (UPD) of the entire chromosome 1. This is the first time a UPD has been described in a patient with schizophrenia, lending further support to involvement of chromosome 1 in schizophrenia susceptibility in the Afrikaners.
Figures


References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Authors' Web site, http://www.sph.umich.edu/csg/abecasis/public/ (for results of parametric linkage analyses)
-
- Center for Medical Genetics, Marshfield Clinic, http://research.marshfieldclinic.org/genetics/ (for the Marshfield genetic map)
-
- CIDR Human Marker Set, http://www.cidr.jhmi.edu/markerset.html (for marker screening set)
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for schizophrenia)
References
-
- Abecasis GR, Cherny SS, Cardon LR (2001a) The impact of genotyping error on family-based analysis of quantitative traits. Eur J Hum Genet 9:130–134 - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association (1994) DSM-IV: diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 4th ed. American Psychiatric Association, Washington, DC
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

