Targeting Alzheimer's disease genes with RNA interference: an efficient strategy for silencing mutant alleles
- PMID: 14754988
- PMCID: PMC373334
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkh208
Targeting Alzheimer's disease genes with RNA interference: an efficient strategy for silencing mutant alleles
Abstract
Tau and amyloid precursor protein (APP) are key proteins in the pathogenesis of sporadic and inherited Alzheimer's disease. Thus, developing ways to inhibit production of these proteins is of great research and therapeutic interest. The selective silencing of mutant alleles, moreover, represents an attractive strategy for treating inherited dementias and other dominantly inherited disorders. Here, using tau and APP as model targets, we describe an efficient method for producing small interfering RNA (siRNA) against essentially any targeted region of a gene. We then use this approach to develop siRNAs that display optimal allele-specific silencing against a well-characterized tau mutation (V337M) and the most widely studied APP mutation (APPsw). The allele-specific RNA duplexes identified by this method then served as templates for constructing short hairpin RNA (shRNA) plasmids that successfully silenced mutant tau or APP alleles. These plasmids should prove useful in experimental and therapeutic studies of Alzheimer's disease. Our results suggest guiding principles for the production of allele-specific siRNA, and the general method described here should facilitate the production of gene-specific siRNAs.
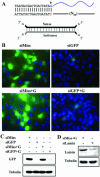
Figures


Similar articles
-
Allele-specific silencing of Alzheimer's disease genes: the amyloid precursor protein genes with Swedish or London mutations.Gene. 2006 Apr 12;371(1):68-74. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2005.11.006. Epub 2006 Jan 19. Gene. 2006. PMID: 16426772
-
Allele-specific silencing of dominant disease genes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Jun 10;100(12):7195-200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1231012100. Epub 2003 Jun 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12782788 Free PMC article.
-
RNA silencing of genes involved in Alzheimer's disease enhances mitochondrial function and synaptic activity.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Dec;1832(12):2368-78. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2013.09.008. Epub 2013 Sep 21. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 24063855 Free PMC article.
-
Do axonal defects in tau and amyloid precursor protein transgenic animals model axonopathy in Alzheimer's disease?J Neurochem. 2006 Aug;98(4):993-1006. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.03955.x. Epub 2006 Jun 19. J Neurochem. 2006. PMID: 16787410 Review.
-
Alzheimer's disease: beta-Amyloid protein and tau.J Neurosci Res. 2002 Nov 1;70(3):392-401. doi: 10.1002/jnr.10355. J Neurosci Res. 2002. PMID: 12391602 Review.
Cited by
-
ASPsiRNA: A Resource of ASP-siRNAs Having Therapeutic Potential for Human Genetic Disorders and Algorithm for Prediction of Their Inhibitory Efficacy.G3 (Bethesda). 2017 Sep 7;7(9):2931-2943. doi: 10.1534/g3.117.044024. G3 (Bethesda). 2017. PMID: 28696921 Free PMC article.
-
Modification of globin gene expression by RNA targeting strategies.Exp Hematol. 2007 Aug;35(8):1209-18. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2007.05.003. Exp Hematol. 2007. PMID: 17662889 Free PMC article.
-
Disease-causing allele-specific silencing by RNA interference.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2013 Apr 11;6(4):522-35. doi: 10.3390/ph6040522. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2013. PMID: 24276122 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrant RNA homeostasis in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: potential for new therapeutic targets?Neurodegener Dis Manag. 2014;4(6):417-37. doi: 10.2217/nmt.14.36. Neurodegener Dis Manag. 2014. PMID: 25531686 Free PMC article.
-
Alzheimer's disease: presence and role of microRNAs.Biomol Concepts. 2016 Aug 1;7(4):241-52. doi: 10.1515/bmc-2016-0014. Biomol Concepts. 2016. PMID: 27505094 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- McManus M.T. and Sharp,P.A. (2002) Gene silencing in mammals by small interfering RNAs. Nature Rev. Genet., 3, 737–747. - PubMed
-
- Song E., Lee,S.K., Wang,J., Ince,N., Ouyang,N., Min,J., Chen,J., Shankar,P. and Lieberman,J. (2003) RNA interference targeting Fas protects mice from fulminant hepatitis. Nature Med., 9, 347–351. - PubMed
-
- Gonzalez-Alegre P., Miller,V.M., Davidson,B.L. and Paulson,H.L. (2003) Toward therapy for DYT1 dystonia: allele-specific silencing of mutant TorsinA. Ann. Neurol., 53, 781–787. - PubMed
-
- Ding H., Schwarz,D.S., Keene,A., Affar,B., Fenton,L., Xia,X., Shi,Y., Zamore,P.D. and Xu,Z. (2003) Selective silencing by RNAi of a dominant allele that causes amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Aging Cell, 2, 209–217. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

