Interstitial cells of Cajal are functionally innervated by excitatory motor neurones in the murine intestine
- PMID: 14754997
- PMCID: PMC1664950
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.058792
Interstitial cells of Cajal are functionally innervated by excitatory motor neurones in the murine intestine
Abstract
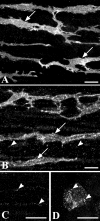
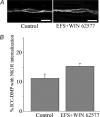
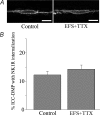
Recent studies have demonstrated that intramuscular interstitial cells of Cajal (ICC) are preferential targets for neurotransmission in the stomach. Terminals of enteric motor neurones also form tight, synaptic-like contacts with ICC in the small intestine and colon, but little is known about the role of these cells in neurotransmission. ICC at the deep muscular plexus (ICC-DMP) of the small intestine express neurokinin 1 receptors (NK1R) and internalize these receptors in response to exogenous substance P. We used NK1R internalization as an assay of functional innervation of ICC-DMP in the murine small intestine. Under basal conditions NK1R-like immunoreactivity (NK1R-LI) was mainly observed in ICC-DMP (519 cells counted, 100% were positive) and myenteric neurones. ICC-DMP were closely apposed to substance P-containing nerve fibres. Of 338 ICC-DMP examined, 65% were closely associated with at least one substance P-positive nerve fibre, 32% were associated with at least two, 2% were associated with more than two nerve fibres and 1% with none. After electrical field stimulation (EFS, 10 Hz; 1 min) NK1R-LI was internalized in more than 80% of ICC-DMP, as compared to 10% of cells before EFS. Internalization of NK1R was not observed in myenteric ICC or smooth muscle cells in response to nerve stimulation. Internalization of NK1R-LI was blocked by the specific NK1 receptor antagonist WIN 62577 (1 microm) and by tetrodotoxin (0.3 microm), suggesting that internalization resulted from stimulation of receptors with neurally released neurokinins. These data suggest that ICC-DMP are primary targets for neurokinins released from enteric motor neurones in the intestine.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Interstitial cells of Cajal in the deep muscular plexus mediate enteric motor neurotransmission in the mouse small intestine.J Physiol. 2006 May 15;573(Pt 1):147-59. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.105189. Epub 2006 Mar 2. J Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16513671 Free PMC article.
-
PKC-epsilon translocation in enteric neurons and interstitial cells of Cajal in response to muscarinic stimulation.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2003 Sep;285(3):G593-601. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00421.2002. Epub 2003 Apr 23. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12711590
-
Activation of neurokinin 1 receptors on interstitial cells of Cajal of the guinea-pig small intestine by substance P.Histochem Cell Biol. 1998 Sep;110(3):263-71. doi: 10.1007/s004180050288. Histochem Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9749960
-
Interstitial cells of Cajal: primary targets of enteric motor innervation.Anat Rec. 2001 Jan 1;262(1):125-35. doi: 10.1002/1097-0185(20010101)262:1<125::AID-AR1017>3.0.CO;2-I. Anat Rec. 2001. PMID: 11146435 Review.
-
Relationships between neurokinin receptor-expressing interstitial cells of Cajal and tachykininergic nerves in the gut.J Cell Mol Med. 2006 Jan-Mar;10(1):20-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2006.tb00288.x. J Cell Mol Med. 2006. PMID: 16563219 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Curcumin relieves mice gastric emptying dysfunction induced by L-arginine and atropine through interstitial cells of Cajal.Exp Ther Med. 2021 Jun;21(6):548. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.9980. Epub 2021 Mar 24. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 33850520 Free PMC article.
-
A deficiency of gastric interstitial cells of Cajal accompanied by decreased expression of neuronal nitric oxide synthase and substance P in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.J Gastroenterol. 2006 Nov;41(11):1076-87. doi: 10.1007/s00535-006-1909-8. Epub 2006 Dec 8. J Gastroenterol. 2006. PMID: 17160518
-
Serotonin augments gut pacemaker activity via 5-HT3 receptors.PLoS One. 2011;6(9):e24928. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024928. Epub 2011 Sep 15. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21949791 Free PMC article.
-
Excitatory Neuronal Responses of Ca2+ Transients in Interstitial Cells of Cajal in the Small Intestine.eNeuro. 2018 Apr 6;5(2):ENEURO.0080-18.2018. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0080-18.2018. eCollection 2018 Mar-Apr. eNeuro. 2018. PMID: 29632869 Free PMC article.
-
Interstitial cells of cajal are involved in neurotransmission in the gastrointestinal tract.Acta Histochem Cytochem. 2006 Dec 28;39(6):145-53. doi: 10.1267/ahc.06023. Epub 2006 Dec 6. Acta Histochem Cytochem. 2006. PMID: 17327901 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Daniel EE, Posey-Daniel V. Neuromuscular structures in opossum esophagus : role of interstitial cells of Cajal. Am J Physiol. 1984;246:G305–G315. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

