Propagation of pacemaker activity in the guinea-pig antrum
- PMID: 14754999
- PMCID: PMC1664942
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.059055
Propagation of pacemaker activity in the guinea-pig antrum
Abstract
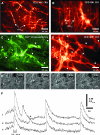
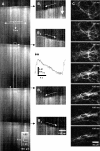
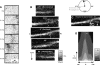
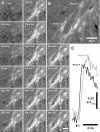
Cyclical periods of depolarization (slow waves) underlie peristaltic contractions involved in mixing and emptying of contents in the gastric antrum. Slow waves originate from a myenteric network of interstitial cells of Cajal (ICC-MY). In this study we have visualized the sequence and propagation of Ca(2+) transients associated with pacemaker potentials in the ICC network and longitudinal (LM) and circular muscle (CM) layers of the isolated guinea-pig gastric antrum. Gastric antrum was dissected to reveal the ICC-MY network, loaded with Fluo-4 AM and activity was monitored at 37 degrees C. Ca(2+) waves propagated throughout the ICC-MY network at an average velocity of 3.24 +/- 0.12 mm s(-1) at a frequency of 4.87 +/- 0.16 cycles min(-1) (n= 4). The propagation of the Ca(2+) wave often appeared 'step-like', with separate regions of the network being activated after variable delays. The direction of propagation was highly variable (Delta angle of propagation 44.3 +/- 10.9 deg per cycle) and was not confined to the axes of the longitudinal or circular muscle. Ca(2+) waves appeared to spread out radially from the site of initiation. The initiating Ca(2+) wave in ICC-MY was correlated to secondary Ca(2+) waves in intramuscular interstitial cells of Cajal, ICC-IM, and smooth muscle cells, and the local distortion (contraction) in a field of view. TTX (1 microm) had little effect on slow wave or pacemaker potential activity, but 2-APB (50 microm) blocked all Ca(2+) waves, indicating a pivotal role for intracellular Ca(2+) stores. Nicardipine (2 microm) eliminated the Ca(2+) transient generated by smooth muscle, but did not affect the fast upstroke associated with ICC-MY. These results indicate that slow waves follow a sequence of activation, beginning with the ICC-MY and ICC-IM network, followed later by a sustained Ca(2+) transient in the muscle layers that is responsible for contraction.
Figures




References
-
- Bauer AJ, Publicover NG, Sanders KM. Origin and spread of slow waves in canine gastric antral circular muscle. Am J Physiol. 1985;249:G800–G806. - PubMed
-
- Burns AJ, Herbert TM, Ward SM, Sanders KM. Interstitial cells of Cajal in the guinea-pig gastrointestinal tract as revealed by c-Kit immunohistochemistry. Cell Tissue Res. 1997;290:11–20. - PubMed
-
- Dickens EJ, Edwards FR, Hirst GDS. Vagal inhibitory projections to rhythmically active cells in the antral region of guinea-pig stomach. Am J Physiol. 2000;279:G388–G399. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

