Achieving antigen-specific immune regulation
- PMID: 14755329
- PMCID: PMC324549
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI20963
Achieving antigen-specific immune regulation
Abstract
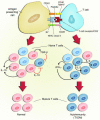
A study in this issue of the JCI shows that in response to autoantigens consisting of peptides from normal proteins, patients with diabetes mount a T cell response characterized by production of IFN-gamma (see the related article beginning on page 451). However, in response to these same antigens, T cells from normal control subjects produce IL-10. The antigen-specific response characterized by release of a regulatory cytokine suggests a mechanism for the control of autoimmunity that is initiated at the time of antigen presentation.
Figures
Comment on
-
Autoreactive T cell responses show proinflammatory polarization in diabetes but a regulatory phenotype in health.J Clin Invest. 2004 Feb;113(3):451-63. doi: 10.1172/JCI19585. J Clin Invest. 2004. PMID: 14755342 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Diabetes Epidemiology Research International Group. Geographic patterns of childhood insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1988;37:1113–1119. - PubMed
-
- Hypponen E, Laara E, Reunanen A, Jarvelin MR, Virtanen SM. Intake of vitamin D and risk of type 1 diabetes: a birth-cohort study. Lancet. 2001;358:1500–1503. - PubMed
-
- Ziegler AG, Schmid S, Huber D, Hummel M, Bonifacio E. Early infant feeding and risk of developing type 1 diabetes-associated autoantibodies. JAMA. 2003;290:1721–1728. - PubMed
-
- Norris JM, et al. Timing of initial cereal exposure in infancy and risk of islet autoimmunity. JAMA. 2003;290:1713-–1720. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

